Lifecycle: from birth (pre-mounting) and death (unmounting).
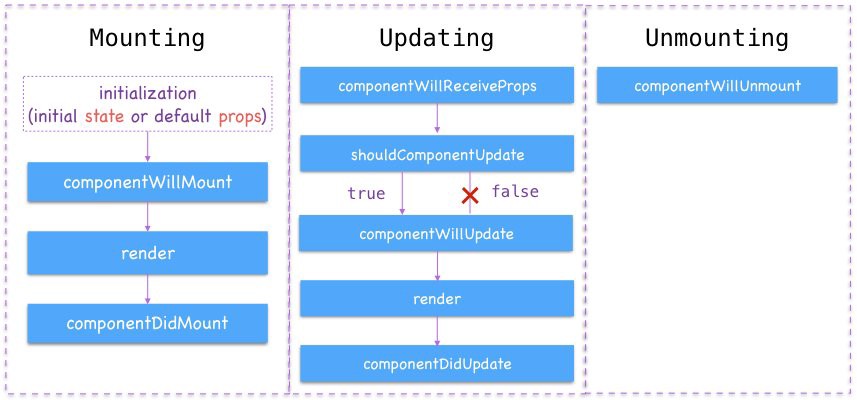
Mounting Method
render
- 「The render function should be pure」,這是使用render很重要的一件事情,要保持render的乾淨,不能在裡面使用setState,也就是不在render()中修改state,或是和瀏覽器互動
constructor(props)
- 這個方法會在component還沒有被mount到畫面上,就先執行一次,也就是建構子。
- 如果state會根據props來設定,也可以在初始化state的時候直接使用props。
constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { color: props.initialColor }; }
componentWillMount
- Most Common Use Case: App configuration in your root component.
- Can call setState: No.. Use default state instead.
- you can’t do anything involving the DOM.
- Setting default state using a constructor.
- That means 99% of your components should probably not use componentWillMount.
- You may see people using componentWillMount to start AJAX calls to load data for your components. Don’t do this. We’ll get to that in the second.
componentDidMount
- Most Common Use Case: Starting AJAX calls to load in data for your component.
- Can call setState: Yes. is where you load in your data
- is also where you can do all the fun things you couldn’t do when there was no component to play with.
- draw on a <canvas> element that you just rendered
- initialize a masonry grid layout from a collection of elements
- add event listeners
- Basically, here you want to do all the setup you couldn’t do without a DOM, and start getting all the data you need.
- 這個方法會在render()之後立即執行
- 如果使用了redux之類的數據服務,這裡可以出發加載服務器數據的action
- 這裡可以使用
setState()方法觸發重新渲染(re-render) - 會在component被mount在畫面上後執行,很適合做跟DOM有關的初始化操作,例如:執行i18n的localize,或是AJAX後端的API,或是window.addEventListener...等。
Updating Method
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps)
- Most Common Use Case: Acting on particular prop changes to trigger state transitions.
- Can call setState: Yes.
- new props arrive 接收到新props時觸發,這方法會在父元件更新props後執行
- 它會接收新的props(nextProps)當參數,如果state會根據props有所改變,那麼在update props的時候,也可以在這個方法裡做setState。
- 這個方法有可能在props沒有改變的時候被觸發,因為父元件有可能重新re-render這個component導致,所以在setState的時候,可以先比較一下this.props和nextProps,避免不必要的re-render。
- Perhaps some data that was loaded in by a parent component’s componentDidMount finally arrived, and is being passed down.
- We are now in a fun place, where we have access to both the next props (via nextProps), and our current props (via this.props).
- Here’s what we should do:
- check which props will change (big caveat with componentWillReceiveProps — sometimes it’s called when nothing has changed; React just wants to check in)
- If the props will change in a way that is significant, act on it
- One more caveat — componentWillReceiveProps is not called on initial render.
- 已掛載的元件收到新的
props時被觸發。在這個方法裡你通常會去比較this.props和nextProps然後再用this.setState去改變狀態。 - React可能會在porps傳入時即使沒有發生改變的時候也發生重新渲染, 所以如果你想自己處理改變,請確保比較props當前值和下一次值; 這可能造成組件重新渲染
- 如果你只是調用
this.setState()而不是從外部傳入props,那麼不會觸發componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps)函數;這就意味著:this.setState()方法不會觸發componentWillReceiveProps(),props的改變或者props沒有改變才會觸發這個方法 - props是父組件傳遞給子組件的。父組件發生render的時候子組件就會調用componentWillReceiveProps
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) { if (this.props.initialColor !=== nextProps.initialColor) { this.setState = ({ color: props.initialColor }); } }
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
- Most Common Use Case: Controlling exactly when your component will re-render.
- Can call setState: No.
- Now our component is getting nervous.
- We have new props. Typical React dogma says that when a component receives new props, or new state, it should update.
- component is going to ask permission first.
- shouldComponentUpdate should always return a boolean
- The default is that it always returns true.
- is an awesome place to improve performance.
- we talk about having a table with many many fields. The problem was that when the table re-rendered, each field would also re-render, only update if the props you care about change.
- 這個方法在首次渲染時不會觸發
- 個方法如果返回
false,那麼props或state發生改變的時候會阻止子組件發生重新渲染; - 目前,如果
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)返回false,那麼componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState),render(),componentDidUpdate()都不會被觸發; - 組件掛載之後,每次調用setState後都會調用shouldComponentUpdate判斷是否需要重新渲染組件。默認返回true,需要重新render。在比較複雜的應用裡,有一些數據的改變並不影響界面展示,可以在這裡做判斷,優化渲染效率。
- 這個方法會在接收到新的props和state之後,在觸發re-render之前,會return是否要re-render畫面的boolean,預設是return true。
- 通常不希望畫面re-render的時候,可以比較目前props與next props,目前state與next state,確定真的有值不同才return true,如果沒有不同則return false。
- 一般來說是在調教效能的時候使用,因為不希望畫面做不必要的re-render,React也提供React.PureComponent,來幫忙判斷shouldComponentUpdate比對的結果
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
- Most Common Use Case: Used instead of(用來代替)componentWillReceiveProps on a component that also has shouldComponentUpdate (but no access使用,存取 to previous props).
- Can call setState: No.
- Now we’ve committed to updating. “Want me to do anything before I re-render?”
- we never use componentWillUpdate.
- Functionally, it’s basically the same as componentWillReceiveProps
- except you are not allowed to call this.setState.
- If you were using shouldComponentUpdate AND needed to do something when props change, componentWillUpdate makes sense.
componentWillUpdate:例如在上面shouldComponentUpdate你回傳了true,元件確定要更新了,在準備更新前這個方法會被觸發。- 如果有根據props改變設定的state,就像前面提到的,需要在componentWillReceiveProps使用。
componentDidUpdate
- Most Common Use Case: Updating the DOM in response to prop or state changes.
- Can call setState: Yes.
- can do the same stuff we did in componentDidMount :reset our masonry layout, redraw our canvas, etc.
- Here’s why: in componentDidUpdate, you don’t know why it updated.
- we want to rearrange the grid after the DOM itself updates — so we use componentDidUpdate to do so.
- 它會在component被update之後執行,它在第一次render()完之後不會觸發,只有"upate"後才會。在這邊可以重新執行根據props或是state更新後,DOM需要改變的變化,例如:重新執行i18n的localize,或是AJAX後端的API...等
-
首次render之後調用componentDidMount,其它render結束之後都是調用componentDidUpdate。
componentWillUnmount
- Most Common Use Case: Cleaning up any leftover debris from your component.
- Can call setState: No.
- can cancel any outgoing network requests, or remove all event listeners associated with the component.
- 當component裡面有做setInterval,或是addEventListener...等,在componentDidMount()裡面做的設定,若需要被終止、移除、清理,就需要在這個方法中執行,例如clearInterval、removeEventListener...等。
Conclusion(Recap)
- can call setState: 1. componentDidMount 2.componentWillReceiveProps 3.componentDidUpdate
- sometimes you need to exact a little more control over how and when your component is updating.
- 記住,不要在render裡面修改state。
- 內建LifeCycle裡的方法, this 都指向component本身,若是自訂新增的方法,則需使用bind指定this,或是Arrow function讓this自動綁定。
引用:
https://goo.gl/TpkCvx
https://goo.gl/1LVKri
https://goo.gl/hMaKHV
https://goo.gl/47tss4
https://goo.gl/o3QFYG
https://goo.gl/hMaKHV