這篇會介紹:
- 為何要使用 config.ini
- Variables 在 *** Settings ***
- 如何使用 config.ini
安安 我來填坑了

為什麼要使用 config.ini
透過 config.ini 可以
- 根據環境定義不同的環境變數
- 避免將機敏資料寫在程式碼中
- 避免第三方服務變更時,有大量的檔案需要被變更
一般來說在開發任何的程式時都會有環境的區別,使用 config 檔案可以,除了環境的區別之外,還有不適合直接寫在程式碼中的資料例如:token、API 的 URL 等
Variables 在 *** Settings ***
在知道如何使用 config.ini 之前須要先知道 Variables 在 Settings 中的作用是什麼
根據 Robot Framework 的文件可以看到 Variables 有兩種方式可以透過 .py 引入變數
- Getting variables directly from a module
- Getting variables from a special function
Getting variables directly from a module 的方式
官方定義:
Variables are specified as module attributes. In simple cases, the syntax is so simple that no real programming is needed. For example, creates a variable with the specified text as its value. One limitation of this approach is that it does not allow using arguments.MY_VAR = 'my value'${MY_VAR}
以官方定義來說就可以直接看到這個方式的缺點就是沒有支援使用 arguments.MY_VAR 的方式使用變數
以範例來看使用這種方式的結果會是這樣
python 的程式碼:
MY_NAME = "SQZ777"
.robot 的程式碼如下
*** Settings ***
Variables test_variables.py
*** Test Cases ***
Test variable in python
Log To Console My Name In Python File Is ${_MY_NAME}
執行結果就可以看到
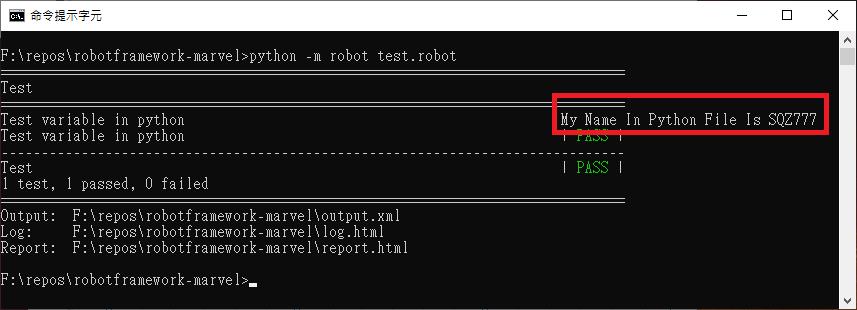
Getting variables from a special function 的方法
官方定義:
An alternative approach for getting variables is having a special function (also camelCase syntax is possible) in a variable file. If such a function exists, Robot Framework calls it and expects to receive variables as a Python dictionary or a Java with variable names as keys and variable values as values. Created variables can be used as scalars, lists, and dictionaries exactly like when getting variables directly from a module, and it is possible to use and prefixes to make creating list and dictionary variables more explicit. The example below is functionally identical to the first example related to getting variables directly from a module.get_variablesgetVariablesMapLIST__DICT__
簡單來說,透過這個方式就可以使變數有「環境」這一層的定義,除此之外還要注意的是,python 的檔案中要定義 function 的名稱為 get_variables
直接來示範吧!
python 的程式碼:
def get_variables():
var = "BLOG_ENV.MY_NAME"
variables = {}
variables[var] = "SQZ777"
return variables
.robot 的程式碼如下
*** Settings ***
Variables test_variables.py
*** Test Cases ***
Test variable in python
Log To Console My Name In Python File Is ${BLOG_ENV.MY_NAME}
在這裡就可以注意到我的變數已經可以隸屬於不同的環境了(BLOG_ENV 中的 MY_NAME)
如何使用 config.ini
了解了兩種不同的引入環境變數的方式終於來到最後了解如何使用 config.ini 的部分啦!
透過 configparser 讀取 config.ini ,再將檔案中所有被定義好的變數回傳給 Robot Framework 就可以達成使用 config.ini 的方法
python 的程式碼:
import configparser
def get_variables(config_path="./config.ini"):
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read(config_path)
variables = {}
print(config.sections)
for section in config.sections():
for key, value in config.items(section):
var = "%s.%s" % (section, key)
variables[var] = value
return variables
config.ini 內容:
[BLOG_ENV]
MARVEL_URL = <http://gateway.marvel.com/>
MARVEL_PUBLIC_KEY = 你的 public key
MARVEL_PRIVATE_KEY = 你的 private key
在 robot 中使用 config,如下圖
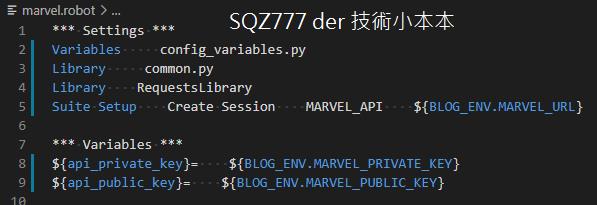
在這裡就會出現一個疑問,這樣不就等於環境被寫死了嗎?

所以這邊為了讓使用上更方便,環境的定義可以透過 command line 來傳入,在執行 Robot Framework 時,代入參數,如下
python -m robot --variable ENV:BLOG_ENV marvel.robot
而 .robot 的檔案則須要改成取用 ENV 這個在 command line 中傳入的變數。
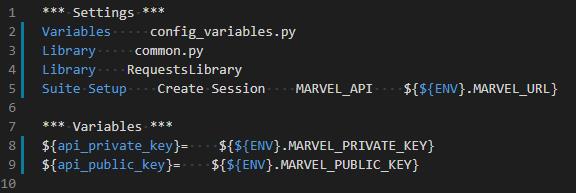
這樣就能執行到指定的環境與變數囉!
感謝收看 <(_ _)>