Log 寫法
Spring Boot uses Apache Commons logging for all internal logging.
Spring Boot’s default configurations provides a support for the use of Java Util Logging, Log4j2, and Logback.
If you are using Spring Boot Starters, Logback will provide a good support for logging. Besides, Logback also provides a use of good support for Common Logging, Util Logging, Log4J, and SLF4J.
Log Format
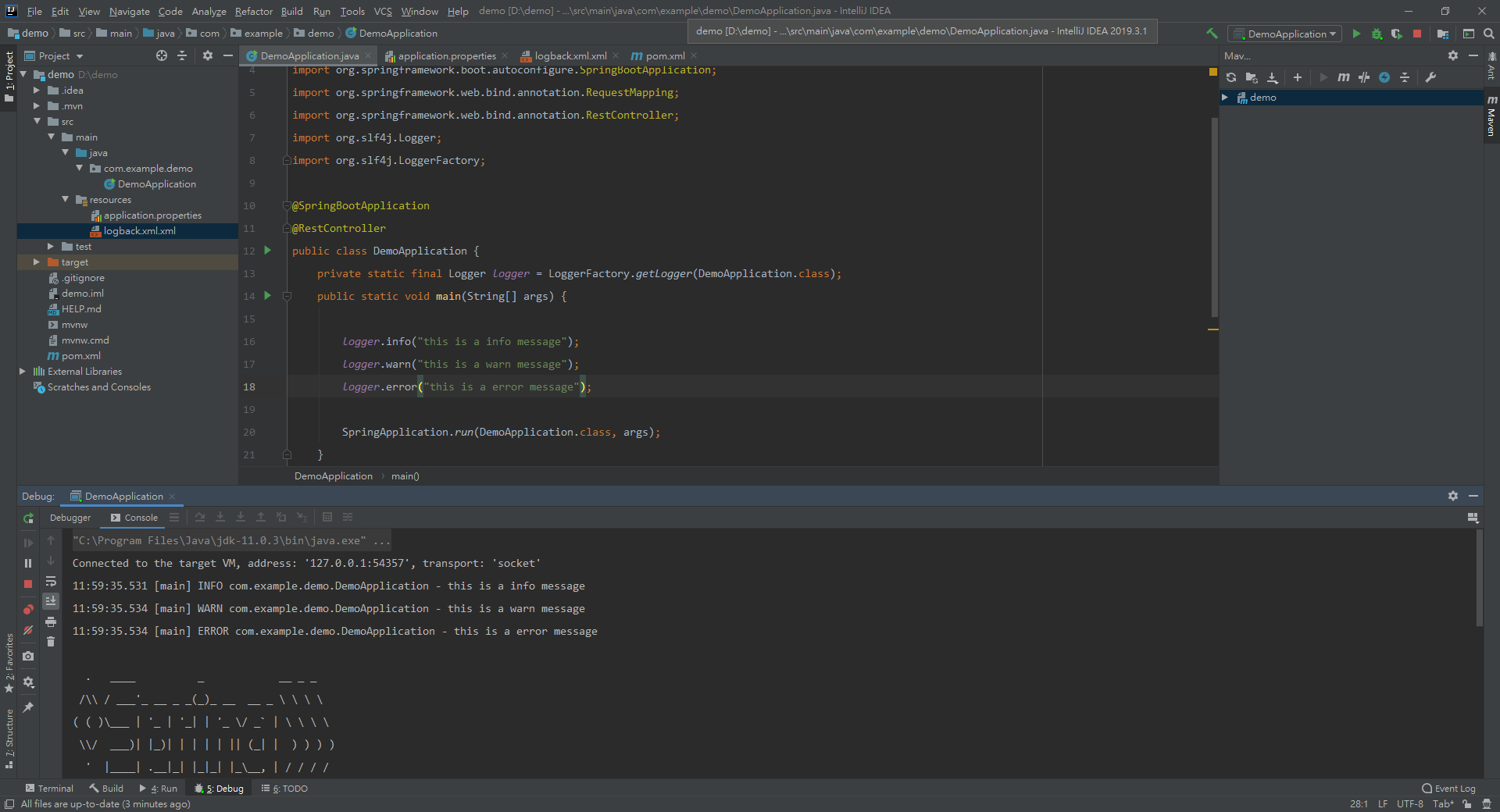
The default Spring Boot Log format is shown in the screenshot given below.

which gives you the following information −
Date and Time that gives the date and time of the log
Log level shows INFO, ERROR or WARN
Process ID
The --- which is a separator
Thread name is enclosed within the square brackets []
Logger Name that shows the Source class name
The Log message
Console Log Output
預設只顯示在螢幕上
The default log messages will print to the console window. By default, “INFO”, “ERROR” and “WARN” log messages will print in the log file.
If you have to enable the debug level log, add the debug flag on starting your application using the command shown below −
java –jar demo.jar --debug
You can also add the debug mode to your application.properties file as shown here −
debug = true
File Log Output
If you want to print the logs in a file, you need to set the property logging.file or logging.path in the application.properties file.
You can specify the log file path using the property shown below. Note that the log file name is spring.log.
logging.path = /var/tmp/
You can specify the own log file name using the property shown below −
logging.file = /var/tmp/mylog.log
Note − files will rotate automatically after reaching the size 10 MB.
You can define the Log pattern in logback.xml file using the code given below. You can also define the set of supported log patterns inside the console or file log appender using the code given below −
<pattern>[%d{yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.sss'Z'}] [%C] [%t] [%L] [%-5p] %m%n</pattern>
The code for complete logback.xml file is given below. You have to place this in the class path.
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <configuration> <appender name = "STDOUT" class = "ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"> <encoder> <pattern>[%d{yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.sss'Z'}] [%C] [%t] [%L] [%-5p] %m%n</pattern> </encoder> </appender> <appender name = "FILE" class = "ch.qos.logback.core.FileAppender"> <File>/var/tmp/mylog.log</File> <encoder> <pattern>[%d{yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.sss'Z'}] [%C] [%t] [%L] [%-5p] %m%n</pattern> </encoder> </appender> <root level = "INFO"> <appender-ref ref = "FILE"/> <appender-ref ref = "STDOUT"/> </root> </configuration>
The code given below shows how to add the slf4j logger in Spring Boot main class file.
package com.tutorialspoint.demo; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DemoApplication.class); public static void main(String[] args) { logger.info("this is a info message"); logger.warn("this is a warn message"); logger.error("this is a error message"); SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); } }
The output that you can see in the console window is shown here −

The output that you can see in the log file is shown here −