[C#]透過PerformanceCounter取得特定Process的CPU使用率
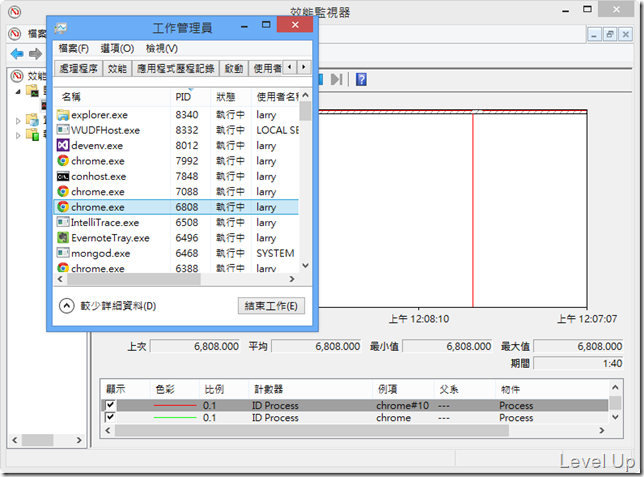
想要透過PerformanceCounter取得特定Process的CPU使用率,首先我們要理解這部分的資料在PerformanceCounter是怎樣分布的。這邊我們可以叫出效能監視器後,找到Process分類,可以看到如下畫面,所有的Process都有對應的Instance,像是chrome、chrome#1、chrome#11...。
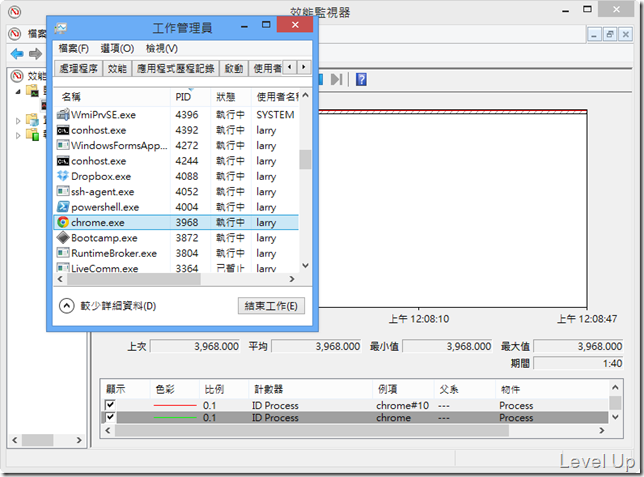
所以我們的第一步就是要從Process找到對應的Process Instance Name。但是BCL內建的Process類別中並未有這樣的資訊,要怎樣找到呢?這邊可透過另一個名叫ID Process的PerformanceCounter輔助,對照筆者準備的兩張圖,不難發現該PerformanceCounter的值對應的就是Process的PID。
這給我們了一個提示,我們可透過這個這個PerformanceCounter反查到Process的Instance Name,像是下面這樣:
private string GetProcessInstanceName(int pid)
{
var category = new PerformanceCounterCategory("Process");
var instances = category.GetInstanceNames();
foreach (var instance in instances)
{
using (var counter = new PerformanceCounter(category.CategoryName,
"ID Process", instance, true))
{
int val = (int)counter.RawValue;
if (val == pid)
{
return instance;
}
}
}
throw new ArgumentException("Invalid pid!");
}
取得了Process的Instance Name後,CPU的使用率我們就可以透過另一個名為% Processor Time的PerformanceCounter下去取得,像是下面這樣:
private static int GetCpuUsage(int pid)
{
if (!m_CounterPool.ContainsKey(pid))
{
m_CounterPool.Add(pid, new PerformanceCounter("Process", "% Processor Time", GetProcessInstanceName(pid)));
}
var lastUpdateTime = default(DateTime);
m_UpdateTimePool.TryGetValue(pid, out lastUpdateTime);
var interval = DateTime.Now - lastUpdateTime;
if (interval.TotalSeconds > 1)
{
m_CpuUsagePool[pid] = (int)(m_CounterPool[pid].NextValue() / Environment.ProcessorCount);
}
return m_CpuUsagePool[pid];
}
這邊要特別注意的是,Query PerformanceCounter的時候,必須要間隔一秒,不然會一直Query到錯誤的值。還有就是取得的值必須要除以核心數才會是我們期望的值。
為了方便重用,依慣例筆者還是稍微整理了一下擴充方法:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public static class ProcessExtension
{
#region Private Static Var
private static Dictionary<int, PerformanceCounter> _counterPool;
private static Dictionary<int, DateTime> _updateTimePool;
private static Dictionary<int, int> _cpuUsagePool;
#endregion
#region Private Static Property
private static Dictionary<int, PerformanceCounter> m_CounterPool
{
get
{
return _counterPool ?? (_counterPool = new Dictionary<int, PerformanceCounter>());
}
}
private static Dictionary<int, DateTime> m_UpdateTimePool
{
get
{
return _updateTimePool ?? (_updateTimePool = new Dictionary<int, DateTime>());
}
}
private static Dictionary<int, int> m_CpuUsagePool
{
get
{
return _cpuUsagePool ?? (_cpuUsagePool = new Dictionary<int, int>());
}
}
#endregion
#region Private Static Method
private static string GetProcessInstanceName(int pid)
{
var category = new PerformanceCounterCategory("Process");
var instances = category.GetInstanceNames();
foreach (var instance in instances)
{
using (var counter = new PerformanceCounter(category.CategoryName,
"ID Process", instance, true))
{
int val = (int)counter.RawValue;
if (val == pid)
{
return instance;
}
}
}
throw new ArgumentException("Invalid pid!");
}
private static int GetCpuUsage(int pid)
{
if (!m_CounterPool.ContainsKey(pid))
{
m_CounterPool.Add(pid, new PerformanceCounter("Process", "% Processor Time", GetProcessInstanceName(pid)));
}
var lastUpdateTime = default(DateTime);
m_UpdateTimePool.TryGetValue(pid, out lastUpdateTime);
var interval = DateTime.Now - lastUpdateTime;
if (interval.TotalSeconds > 1)
{
m_CpuUsagePool[pid] = (int)(m_CounterPool[pid].NextValue() / Environment.ProcessorCount);
}
return m_CpuUsagePool[pid];
}
#endregion
#region Public Static Method
public static string GetInstanceName(this Process process)
{
return GetProcessInstanceName(process.Id);
}
public static int GetCpuUsage(this Process process)
{
return GetCpuUsage(process.Id);
}
#endregion
}
已筆者的測試範例來說,撰寫起來會像下面這樣:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication24
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
timer1.Interval = 1000;
lbxProcess.DisplayMember = "ProcessName";
lbxProcess.DataSource = Process.GetProcesses();
}
private void lbxProcess_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var selectedProcess = lbxProcess.SelectedItem as Process;
if (selectedProcess == null)
return;
timer1.Enabled = false;
tbxInstanceName.Text = selectedProcess.GetInstanceName();
tbxCPU.Text = selectedProcess.GetCpuUsage().ToString();
timer1.Enabled = true;
}
private void timer1_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var selectedProcess = lbxProcess.SelectedItem as Process;
if (selectedProcess == null)
return;
tbxCPU.Text = selectedProcess.GetCpuUsage().ToString();
}
}
}
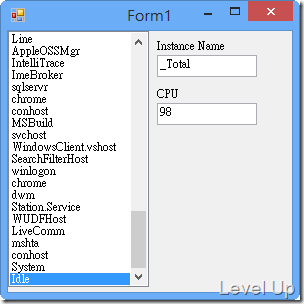
運行結果:
_thumb.png)