在設計Angular程式的時候,我們可以在各種基本的表單上加入[(ngModel)]來達到two way binding的效果,不過如果想要在Component中也能使用[(mgModel)]該怎麼辦呢?今天就來談談如何讓自訂的Component也可以直接使用ngModel達到two way binding!
功能說明
先看下圖,假設我們有一個UserProfile的Component,可以傳入一個使用者的個人資料,並且能夠在Component中編輯

app.component.html目前的程式如下
<app-user-profile></app-user-profile>
<pre>{{ user | json }}</pre>
接下來問題來了,我們要如何能把user透過ngModel傳到UserProfile這個Component中呢?基本上只有幾個主要步驟:
1. 宣告一個包含NG_VALUE_ACCESSOR的provider
首先我們在UserProfileComponent中加入以下程式
import { NG_VALUE_ACCESSOR, ControlValueAccessor } from '@angular/forms';
import { Component, OnInit, forwardRef } from '@angular/core';
export const USER_PROFILE_VALUE_ACCESSOR: any = {
provide: NG_VALUE_ACCESSOR,
useExisting: forwardRef(() => UserProfileComponent),
multi: true
};
然後在@Component宣告中加入這個provider
@Component({
selector: 'app-user-profile',
templateUrl: './user-profile.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./user-profile.component.css'],
providers: [USER_PROFILE_VALUE_ACCESSOR]
})
以上步驟會告訴Angular核心我們所使用的Component可以被視為一個擴充的表單控制項,因此就可以搭配使用[(ngModel)]以及[formControl],記得forwardRef(() => UserProfileComponent)要改成我們要使用的Component,Angular的DI機制會找到所有擴充NG_VALUE_ACCESSOR的來源,並把它視為表單控制項來使用。
因此以上的動作可以簡單想像為:將我們Component聲明成為與input,select等相同的表單控制項,以供[(ngModel)]以及[formControl]使用。
2. 實做ControlValueAccessor
將Component聲明為表單控制項之後,我們還必須讓提供幾個方法讓Angular在資料變更時能進行two way binding的工作,我們必須在component中提供4個方法,這4個方法來自ControlValueAccessor
- writeValue(obj: any): void:當來源資料變更時呼叫
- registerOnChange(fn: any): void:提供Component內資料變更需要binding時呼叫的方法,會Component初始化時傳一個function當作參數,我們需要在Component內保留此變數,在資料變需要綁定時進行呼叫。
- registerOnTouched(fn: any): void:同registerOnChange,只不過是在狀態變更為touched時呼叫
- setDisabledState(isDisabled: boolean): void:當控制項的disabled屬性變更時會呼叫的方法
因此我們的Component內容整體如下
import { NG_VALUE_ACCESSOR, ControlValueAccessor } from '@angular/forms';
import { Component, OnInit, forwardRef, Input } from '@angular/core';
export const USER_PROFILE_VALUE_ACCESSOR: any = {
provide: NG_VALUE_ACCESSOR,
useExisting: forwardRef(() => UserProfileComponent),
multi: true
};
@Component({
selector: 'app-user-profile',
templateUrl: './user-profile.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./user-profile.component.css'],
providers: [USER_PROFILE_VALUE_ACCESSOR]
})
export class UserProfileComponent implements ControlValueAccessor {
user: any;
get name() {
return this.user.name;
}
set name(value) {
this.user.name = value;
this.notifyValueChange();
}
get age() {
return this.user.age;
}
set age(value) {
this.user.age = value;
this.notifyValueChange();
}
@Input() disabled: boolean;
onChange: (value) => {};
onTouched: () => {};
constructor() {
this.user = {};
}
notifyValueChange() {
if (this.onChange) {
this.onChange({
name: this.name,
age: this.age
});
}
}
writeValue(obj: any): void {
this.user = obj;
if (!this.user) {
this.user = {};
}
}
registerOnChange(fn: any): void {
this.onChange = fn;
}
registerOnTouched(fn: any): void {
this.onTouched = fn;
}
setDisabledState(isDisabled: boolean): void {
this.disabled = isDisabled;
}
}
除了4個ControlValueAccessor的實做之外,我們加入一個notifyValueChange()方法,負責在資料變更時將要綁定的資料透過registerOnChange時傳過來的方法傳遞回去。而在Component中當資料被設定時(setter)在乎叫這個方法,來完成通知變更的動作。
接著把app.component.html的內容修改成:
<app-user-profile [disabled]="profileDisabled" [(ngModel)]="user"></app-user-profile>
<div><button (click)="profileDisabled = !profileDisabled">Disable</button></div>
<pre>{{ user | json }}</pre>
最終產生執行成果如下圖:
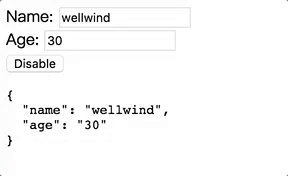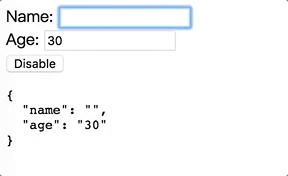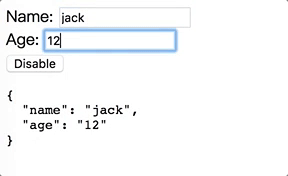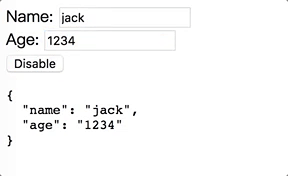
我們終於能夠讓Component也能夠支援[(ngModel)]啦!
完整的程式碼在此:https://github.com/wellwind/angular-advanced-topic-demo/tree/master/customize-component-with-ngmodel
單元回顧
今天我們介紹了如何在Component中直接加入[(ngModel)]達到two way binding的方法,有了two way binding可以讓其他使用Component的程式少寫一些程式碼,這在撰寫常用的共用元件,或是專門在寫Component給他人使用的情境下非常實用!提供給需要的朋友參考囉!
參考資料:
https://blog.thoughtram.io/angular/2016/07/27/custom-form-controls-in-angular-2.html
http://almerosteyn.com/2016/04/linkup-custom-control-to-ngcontrol-ngmodel
https://angular.io/docs/ts/latest/api/forms/index/ControlValueAccessor-interface.html
2017/08/15補充:實作ControlValueAccessor的方式可以讓我們的Component被當作表單控制項,因此會有disabled的功能,再內容異動時,Angular也會幫我們加上touched、dirty等屬性,非常方便。不過若不需要這些功能的話,有更簡單達到two way binding的方法,可以參考以下文章:
[Angular] Two-way Binding 的運作方式 (上一篇文章的原理解釋)