疊(迭)代(Iter):
- 目的通常是為了接近所需求的目標或結果。
- 每一次對過程的重複被稱為一次"疊代",
- 每一次疊代得到的結果通常會被用來作為下一次疊代的初始值。
- 使用疊代方式讀取字串->next 一次讀一個字元
- 使用疊代方式讀取陣列->next 一次讀一筆資料
- 在類別中使用疊代
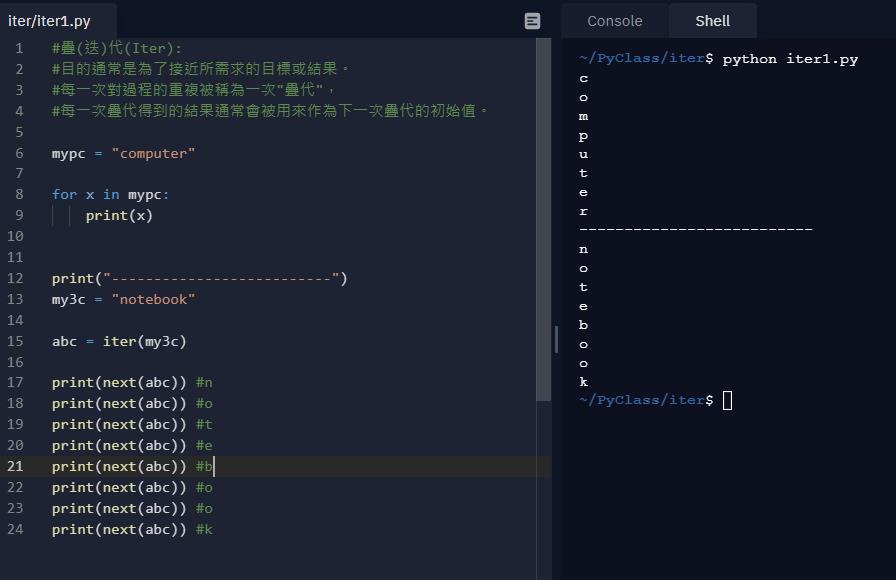
使用疊代方式讀取字串->next 一次讀一個字元
mypc = "computer"
for x in mypc:
print(x)
print("--------------------------")
my3c = "notebook"
abc = iter(my3c)
print(next(abc)) #n
print(next(abc)) #o
print(next(abc)) #t
print(next(abc)) #e
print(next(abc)) #b
print(next(abc)) #o
print(next(abc)) #o
print(next(abc)) #k
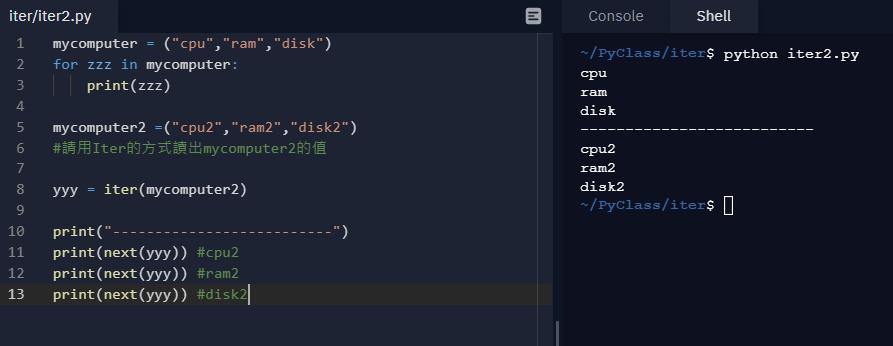
使用疊代方式讀取陣列->next 一次讀一筆資料
mycomputer = ("cpu","ram","disk")
for zzz in mycomputer:
print(zzz)
mycomputer2 =("cpu2","ram2","disk2")
#請用Iter的方式讀出mycomputer2的值
yyy = iter(mycomputer2)
print("--------------------------")
print(next(yyy)) #cpu2
print(next(yyy)) #ram2
print(next(yyy)) #disk2
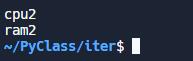
搭配for迴圈只讀前兩筆資料
for _ in range(2):
print(next(yyy)) #只讀前兩筆如果key值為空可以使用底線 _
在類別中使用疊代
#有__iter__ 就一定有__next__ (它們是一組的)
class mydouble:#類別
def __iter__(self): #疊代(類別變數)
self.num = 2 #類別裡面的num(變數)等於2
return self #返回所有的類別變數 #2
def __next__(self):
zz = self.num #zz =2
self.num += 2
return zz #>>2 >>4 >>6 >>......
#物件 = 呼叫類別
calldouble = mydouble()#呼叫類別
#變數 = 疊代(物件)
calliter = iter(calldouble)
#使用next讀
print(next(calliter))#2
print(next(calliter))#4
print(next(calliter))#6
print(next(calliter))#8
print(next(calliter))#10
print(next(calliter))#12
print(next(calliter))#14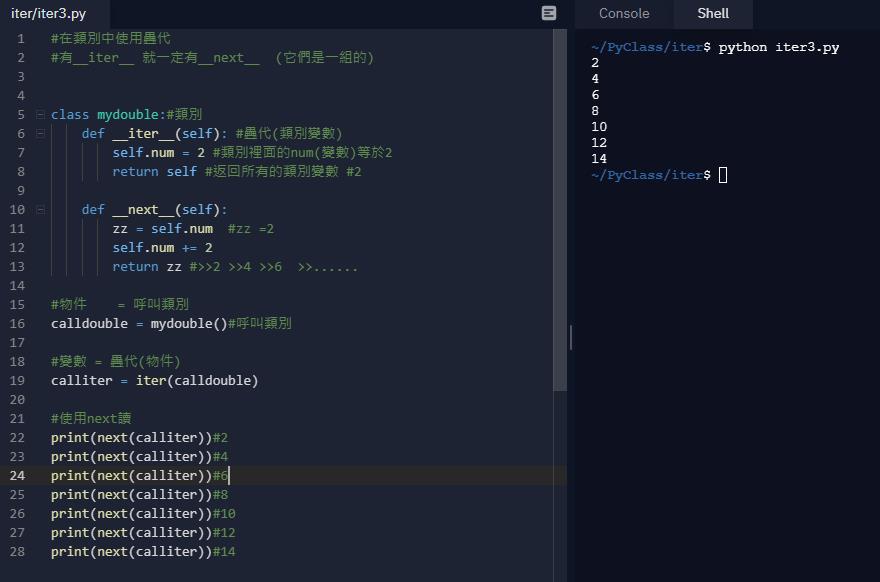
Yiru@Studio - 關於我 - 意如
