Windows Phone 8 - App2App Communication - File associations
在前一篇<Windows Phone 8 - App2App Communication - Protocol (URI Schema)>已經介紹過WP8 SDK
應用程式之間的互動的方式:(2) URI Schema;另一個要介紹的方式:File Associations,WP8允許應用程式註冊
針對某一檔案類型(file extensions)進行處理,目的在於是針對特定檔案類型時,可以觸動其他程式來進行處理的任務。
另外,File Associations也被用於決定那些file types apps可以使用External storage APIs讀取SD Card中的檔案。
但要注意File associations只能註冊處理某特定檔案類型,註冊的類型不會被系統或其他應用程式拿來使用。
那麼File Associations運作的概念是什麼呢?
‧當沒有Apps支援特定的file extensions時,marketplace將會被啟動並允許用戶下載支援該file extensions的Apps;
‧如果系統只有一個App註冊該file extensions時,該Apps會自動被開啟,並且是使用Read-Only的copy放式傳給App;
‧如果超過一個App註冊該file extensions時,系統顯示一個對話框供用戶選擇要使用的App;
‧啟動File Associations的情境,可來自:
->電子郵件的附件;
->使用Internet Explorer瀏覽網頁中的檔案;
->來自Near Field Communications (NFC) tag;
->其他應用程式互動;
〉File Association:
運作方式是如何呢?應用程式必須註冊一個File Extension對象以處理與告知系統如何轉到該應用程式進行讀取。
不過要特別注意,有些系統內定的File extensions會有自行處理的方式,例如:Internet Explorer覆寫File Associations,
讓Audio/或Video/的檔案類型可以啟動內鍵的Media player(zune player)。所以自己的App如果有監聽這一類的檔案,
透過Internet Explorer來觸發file associations是不會開啟自己的App,但如果用其他App將會正常找到自己的App。
接下來討論要完成這樣的註冊,將分成以下幾個步驟來實作:
(1) 在WMAppManifest.xml註冊需要的File extensions與Logos(小、中、大);
(2) 處理由系統根據file associations將特定的Deep link URI送至指定的App;
(A) 至WMAppManifest.xml的<Extension />標籤中註冊要支援的File Extension:
以下先指定出相關設定標籤與屬性的定義說明:
| Element | Parent element | Description |
| Extensions | App | 必須加入在<Tokens />的下方。 |
| FileTypeAssociation | Extensions | 描述File association。最多可以註冊20個File associations。 ‧Name屬性:必要值,可以自行定義; ‧TaskID:預設為:_default; ‧NavUriFragement:定義要傳送的Query Token; |
| Logos | FileTypeAssociation | 選擇使用的element。列出file associations使用的logos。 |
| Logo | Logos | 選擇使用的Element。列出三種需要的圖示大小。如果有提供的話,IsRelative屬性必須存在,並且等於true。 |
| SupportedFileType | FileTypeAssociation | 列出該file association的所有的file extensions。 |
| FileType | SupportedFileType | 列出該file extension使用的file type,需包括「.」的符號,每一個file association最多具有20個file extensions。如果app讀取的檔案來自SD Card,必須指定ContentType屬性來描述該file extension。 |
範例如下:
1: <Extensions>
2: <FileTypeAssociation Name="RecipeLaunch" TaskID="_default"
3: NavUriFragment="fileToken=%s">
4: <SupportedFileTypes>
5: <FileType>.rcp</FileType>
6: <FileType>.recipe</FileType>
7: </SupportedFileTypes>
8: </FileTypeAssociation>
9: </Extensions>
在使用<FileTypeAssociation />標籤時,在<SupportedFileTypes />標籤下可以接收最多20個<FiletType /> ,
每一個<FileType />代表一個獨立的檔案類型。
<FileTypeAssociation />下定義的這些FileType集合,使用相同的Content Type與Logo icon。這也代表說,
Content Type相同:存取的資料來源均相同;Logo icon相同:當系統出現選擇開啟檔案時,該程式的顯示Icon;
當然,也可以更換File Type的Logos(並非強制),建議可以放置在Assets資料夾裡,宣告三個大小:
‧small:32x32,使用在email的附件顯示;
‧medium:69x69,使用在Office Hub的List views;
‧large:176x176,使用於Web Browser進行Downloads時;
另外,由於file type logos是出現在白色背景上,所以在送審前一定要測試這三個圖示呈現在白色背景上的效果。
註冊相同的file extensions有超過一個以上的應用程式,那將不會看到file type logos出現,改用一個通用的圖示。
以下為範例:
1: <FileTypeAssociation Name="RecipeLaunch" TaskID="_default" NavUriFragment="fileToken=%s">
2: <!-- 指定file type對應的圖示 -->
3: <Logos>
4: <Logo Size="small">SmallFileIcon.png</Logo>
5: <Logo Size="medium">MediumFileIcon.png</Logo>
6: <Logo Size="large">LargeFileIcon.png</Logo>
7: </Logos>
8: <SupportedFileTypes>
9: <FileType>.rcp</FileType>
10: <FileType ContentType="application/recipe">.recipe</FileType>
11: </SupportedFileTypes>
12: </FileTypeAssociation>
[注意]
由於Windows Phone 8支援可從多個地方開啟檔案。如果應用程式本身支援開啟檔案是來自外部儲存空間(如:SD卡),
在宣告要支援的File Type時,要加上ContentType的註冊。如下:
1: <!-- 宣告ContentType來自何種Location的資源 -->
2: <FileType ContentType="application/recipe">.recipe</FileType>
(B) 處理由系統根據file associations將特定的Deep link URI送至指定的App:
當開發的App被啟動以處理特定的file type,系統會轉交一個deep link URI給App的。在這個URI裡藏了相關的資訊,如下:
‧FileTypeAssociation字段,為固定值;
‧NavUriFragment屬性指定的Parameter,以上述的範例為:fileToken=%s,該%s會被替換成實作的GUID;
二個組合起來的結果:「/FileTypeAssociation?fileToken=89819279-4fe0-4531-9f57-d633f0949a19」;
收到GUID後,開發的App需要準備一個Custom URI Mapper搭配SharedStorageAccessManager.GetSharedFileName(),以取得
該GUID實際的file type,接著往下進行需要任務邏輯。例如:如果有多個file extensions需要轉到不同的Page,即可以透過
客製的URI Mapper轉到對應的Page,但也別忘記如果不是File Associations的URI,則直接回傳喔。
以下透過程式碼來說明:
(B-1). 實作Custom URI Mapper:
與實作App2App的URI Schema一樣,需要繼承UriMapperBase類別,並且override它的MapUri()方法,如下:
1: class CusUriMapper : UriMapperBase
2: {
3: private string gTempUri = string.Empty;
4:
5: public override Uri MapUri(Uri uri)
6: {
7: gTempUri = uri.ToString();
8:
9: //判斷是否為File Associations
10: if (gTempUri.Contains("/FileTypeAssociation") == true)
11: {
12: //取得File Id(或GUID)
13: int tFileIdIdx = gTempUri.IndexOf("fileToken=") + 10;
14: string tFileID = gTempUri.Substring(tFileIdIdx);
15:
16: //取得File Name
17: string tIncommingFileName = SharedStorageAccessManager.GetSharedFileName(tFileID);
18: //取得File Extension
19: int tExtenIdx = tIncommingFileName.IndexOf(".");
20: string tIncommingFileType = tIncommingFileName.Substring(tExtenIdx).ToLower();
21:
22: //定義Map相關:.sdkTest1與.sdkTest2至不同的Page
23: switch (tIncommingFileType)
24: {
25: case ".sdkTest1":
26: return new Uri("/Test1Page.xaml?fileToken=" + tFileID, UriKind.Relative);
27: case ".sdkTest2":
28: return new Uri("/Test2Page.xaml?fileToken=" + tFileID, UriKind.Relative);
29: default:
30: return new Uri("/MainPage.xaml", UriKind.Relative);
31: }
32: }
33: //其他非File Associations的URI直接拋轉
34: return uri;
35: }
36: }
實作的範例,識別檔案的副檔名為:.sdkTest1與.sdkTest2分別前往不同的Page進行處理的動作;如果不屬於File
associations的機制,則直接回傳uri不影響其他的應用邏輯。
(B-2). 覆寫應用程式RootFrame的UriMapper元件:
前往App.xaml.cs中的InitializePhoneApplication(),重新設定RootFrame中的UriMapper,如下:
1: // Do not add any additional code to this method
2: private void InitializePhoneApplication()
3: {
4: if (phoneApplicationInitialized)
5: return;
6:
7: // Create the frame but don't set it as RootVisual yet; this allows the splash
8: // screen to remain active until the application is ready to render.
9: RootFrame = new PhoneApplicationFrame();
10: RootFrame.Navigated += CompleteInitializePhoneApplication;
11:
12: //增加自訂的UriMapper
13: RootFrame.UriMapper = new CusUriMapper();
14:
15: // Handle navigation failures
16: RootFrame.NavigationFailed += RootFrame_NavigationFailed;
17:
18: // Handle reset requests for clearing the backstack
19: RootFrame.Navigated += CheckForResetNavigation;
20:
21: // Ensure we don't initialize again
22: phoneApplicationInitialized = true;
23: }
一定要進行這樣的動作,才能讓應用程式在接收到系統傳過來的deep link URI時,有正確的UriMapper進行處理。
而且要記得寫在RootFrame.Navigated設定完畢之後。
實作上述二個步驟後,即完成向系統註冊要處理的File Associations與監控特定的File Extensions,並且實作了當用戶選擇
自己的應用程式時,有自訂的UriMapper來進行處理導向指定的Page,最後就是這些Page要負責的邏輯與運用了。
[實作範例]
1. 註冊需要的File Associations與File Extensions;(參考上述定義)
2. 客製URI Mappers與覆寫RootFrame.UriMapper;(參考上述定義)
3. 實作針對.sdkTest1與.sdkTest2不同類型處理的Page邏輯;
3-1. .sdkTest1處理機制;
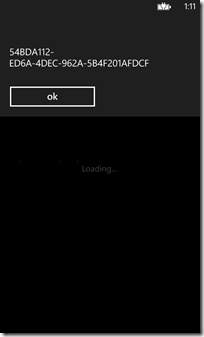
以顯示File Token ID為主要目的,如下程式碼:
1: protected override void OnNavigatedTo(NavigationEventArgs e)
2: {
3: base.OnNavigatedTo(e);
4:
5: if (NavigationContext.QueryString.ContainsKey("fileToken") == true)
6: {
7: string tFileID = NavigationContext.QueryString["fileToken"];
8: MessageBox.Show(tFileID);
9: }
10: }
3-2. .sdkTest2處理機制;
增加將File Token ID的檔案寫入Local folder,並且透過IsolatedStorageStream讀取其檔案透過MeidaElement進行播放;
1: protected override void OnNavigatedTo(NavigationEventArgs e)
2: {
3: base.OnNavigatedTo(e);
4:
5: if (NavigationContext.QueryString.ContainsKey("fileToken") == true)
6: {
7: HandleFileAssociation();
8: }
9: }
10:
11: private async void HandleFileAssociation()
12: {
13: // 取得File Token ID與File Name;
14: string tFileID = NavigationContext.QueryString["fileToken"];
15: string tFileName = SharedStorageAccessManager.GetSharedFileName(tFileID);
16:
17: // 取得目前的local folder;
18: StorageFolder tTargetFolder = await ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder.
19: CreateFolderAsync("FileAss", CreationCollisionOption.OpenIfExists);
20: // 將檔案複製到指定的目錄下, 並且如果有存在的話,就直接覆寫;
21: IStorageFile tFileObj = await SharedStorageAccessManager.
22: CopySharedFileAsync(tTargetFolder, tFileName,
23: NameCollisionOption.ReplaceExisting, tFileID);
24:
25: // 取得檔案內容;由於使用的是MediaElement需要使用IsolatedStorageStream,因此取消下方的程式段;
26: string tFilePath = "/FileAss/134.sdkTest2";
27: UseIsolatedStorage(tFilePath);
28: //IRandomAccessStreamWithContentType tContentStream = await tFileObj.OpenReadAsync();
29: }
30:
31: private void UseIsolatedStorage(string pFilePath)
32: {
33: using (IsolatedStorageFile tIsoFile = IsolatedStorageFile.GetUserStoreForApplication())
34: {
35: // 使用MediaElement需要的IsolatedStorageStream,讀取已經寫入的檔案;
36: using (IsolatedStorageFileStream tIsoStream = new IsolatedStorageFileStream(
37: pFilePath, FileMode.Open, tIsoFile))
38: {
39: mediaElement1.SetSource(tIsoStream);
40: mediaElement1.Play();
41:
42: tblStatus.Text = "Playing...";
43: }
44: }
45: }
4. 實作MainPage.xaml增加LaunchFileAysnc的功能,進行測試;
內有二個按鈕,進行.sdkTest1與.sdkTest2二個測試;
1: private void btnOpenByLaunchUri_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
2: {
3: Button tBtn = sender as Button;
4: if (tBtn.Name == "btn1")
5: OpenFileByAsync("1");
6: else
7: OpenFileByAsync("2");
8: }
9:
10: private async void OpenFileByAsync(string pType)
11: {
12: try
13: {
14: // 注意是使用「\」非「/」
15: string tFileName = @"Files\134.sdkTest" + pType;
16: var tFile = await Package.Current.InstalledLocation.GetFileAsync(tFileName);
17:
18: if (tFile != null)
19: {
20: bool tSuccess = await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchFileAsync(tFile);
21: if (tSuccess)
22: MessageBox.Show("成功啟動檔案");
23: else
24: MessageBox.Show("失敗啟動檔案");
25: }
26: else
27: {
28: MessageBox.Show("沒有找到檔案");
29: }
30: }
31: catch (Exception ex)
32: {
33: MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
34: }
35: }
5. 執行結果:
[範例程式]
=======
[重要元素]
以下針對在處理File Associations時的重要元件加以說明:
該類別來自Windows.Storage.SharedAccess命名空間,提供連結被共享的關聯文件;提供二個方法協助在應用程式取得
來自File Associations得到的File:
| Method | Return Type | Description |
| GetSharedFileName | String | 取得檔案的名稱,包括副檔名。 |
| CopySharedFileAsync | StorageFile | 將Shared的檔案複製到指定的地方,並且取得複製後的檔案物件; |
對於CopySharedFileAsync的使用方式,如下:
1: private async void HandleFileAssociation()
2: {
3: // 取得File Token ID與File Name;
4: string tFileID = NavigationContext.QueryString["fileToken"];
5: string tFileName = SharedStorageAccessManager.GetSharedFileName(tFileID);
6:
7: // 取得目前的local folder;
8: StorageFolder tTargetFolder = await ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder.
9: CreateFolderAsync("FileAss", CreationCollisionOption.OpenIfExists);
10: // 將檔案複製到指定的目錄下, 並且如果有存在的話,就直接覆寫;
11: IStorageFile tFileObj = await SharedStorageAccessManager.
12: CopySharedFileAsync(tTargetFolder, tFileName,
13: NameCollisionOption.ReplaceExisting, tFileID);
14:
15: // 讀取檔案,取得Stream
16: IRandomAccessStreamWithContentType tContentStream = await tFileObj.OpenReadAsync();
17: }
對於SharedAccessManager的操作非常特別,在使用上要注意。
如果有寫過Win8的程式,應該對該指令不陌生;在URI串聯則是使用LaunchUriAsync指令。在WP8也提供在程式裡,
啟動某個file extension的檔案,讓有註冊於系統的File Associations取得通知,使得用戶可以選擇需要的應用程式來執行。
擷取MSDN上的使用方法如下:
1: async void DefaultLaunch()
2: {
3: // 指定檔案的位置,以在install folder為例,
4: // 取得install folder下images資料夾中的檔案;注意是使用「\」,而不是之前WP中使用的「/」;
5: string imageFile = @"images\test.png";
6:
7: // 取得指定的檔案
8: var file = wait Windows.ApplicationModel.Package.Current.
9: InstalledLocation.GetFileAsync(imageFile);
10:
11: if (file != null)
12: {
13: // 啟動檔案
14: var success = await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchFileAsync(file);
15:
16: if (success)
17: {
18: // 檔案被執行
19: }
20: else
21: {
22: // 檔案執行失敗
23: }
24: }
25: else
26: {
27: // 不能找到指定的檔案
28: }
29: }
透過該方法也蠻適用於測試自己應用程式的File Associations是否有設定成功;
======
在處理WP8中的Storage問題,如果扣掉在WP 7.1年代使用的IsolatedStorage,其實新的APIs是很特別的,
這觀念主要來自Win 8 Application的開發模式,如果上述在閱讀上對於檔案比較有興趣的話,可以另外參考
<>與<>有助於了解WP8在Storage的存取方式。
希望以上的介紹有助於大家了解Windows Phone 8 SDK在App-to-App Communication上的特性。謝謝。
References:
‧What's new in Windows Phone 8
‧Communications for Windows Phone
‧Auto-launching apps using file and URI associations for Windows Phone 8 (重要)
‧Reading from the SD card on Windows Phone 8 (重要)
‧windows phone 8 新增功能:从一个应用程序启动另一个程序(file association 和 Protocol association两种方式)
‧Reserved file and URI associations for Windows Phone 8 (重要)
‧Auto Launching Apps now possible using file associations for Windows Phone 8
‧URI schemes for launching built-in apps for Windows Phone 8 (重要)
‧如何接收影像 (使用 C#/VB/C++ 和 XAML 的 Windows 市集應用程式)
‧Playing media content on Windows Phone 7 with MediaElement & Zero Gravity: Moving to WP7