pytest 是一個功能強大且靈活的 Python 測試框架,身為一個開發者學好怎麼寫測試是基本的必要條件,以下是我對 pytest 的使用心得。
開發環境
- Windows 11 Home
- PyCharm 2024.3.5
- Python 3.13.2
- uv 0.6.10
- pytest 8.3.5
- pytest-cov 6.1.0
- pytest-html>=4.1.1
安裝環境
用 uv 建立 python 專案
uv init Lab.Py.TestProject
cd Lab.Py.TestProject
在 python 專案安裝測試套件
uv add pytest
測試起手式
基本原則
建立測試檔案
- 測試類別名稱需以 Test 開頭。
- 測試函數名稱需以 test 開頭。
被測目標物
# calculator.py
class Calculator:
"""
一個簡單的計算器類,提供基本的數學運算功能。
提供的運算包括加法、減法、乘法和除法。
使用範例:
calc = Calculator()
result = calc.add(5, 3)
result = calc.subtract(5, 3)
result = calc.multiply(5, 3)
result = calc.divide(5, 3)
"""
def add(self,a, b):
return a + b
def subtract(self,a, b):
return a - b
def multiply(self,a, b):
return a * b
def divide(self,a, b):
if b == 0:
raise ValueError("除數不能為零")
return a / b
撰寫測試
範例程式碼:
# calculator_test.py
import pytest
from calculator import Calculator
class TestCalculator:
def test_add(self):
target = Calculator()
assert target.add(2, 3) == 5
def test_subtract(self):
target = Calculator()
assert target.subtract(5, 3) == 2
def test_multiply(self):
target = Calculator()
assert target.multiply(4, 3) == 12
def test_divide(self):
target = Calculator()
assert target.divide(10, 2) == 5
驗證/斷言
assert
結果跟期望值比對
assert target.divide(10, 2) == 5
pytest.raises
檢測是否拋出預期的例外。
def test_divide_by_zero(self):
target = Calculator()
with pytest.raises(ValueError):
target.divide(10, 0)
執行測試
測試多個檔案
如果專案包含多個測試檔案,在終端機中執行以下指令:
uv run pytest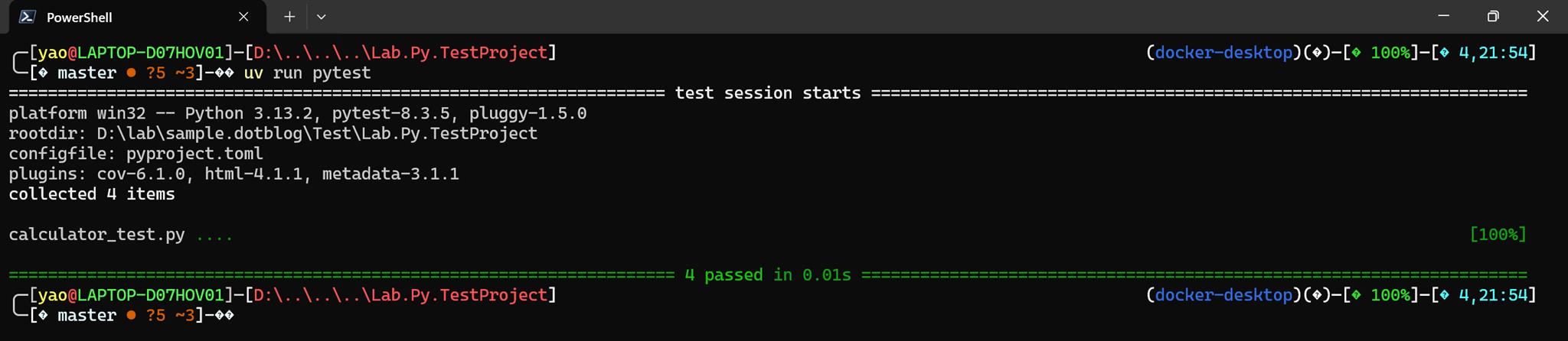
指定特定檔案
uv run pytest test_example.py
顯示詳細測試結果
uv run pytest -v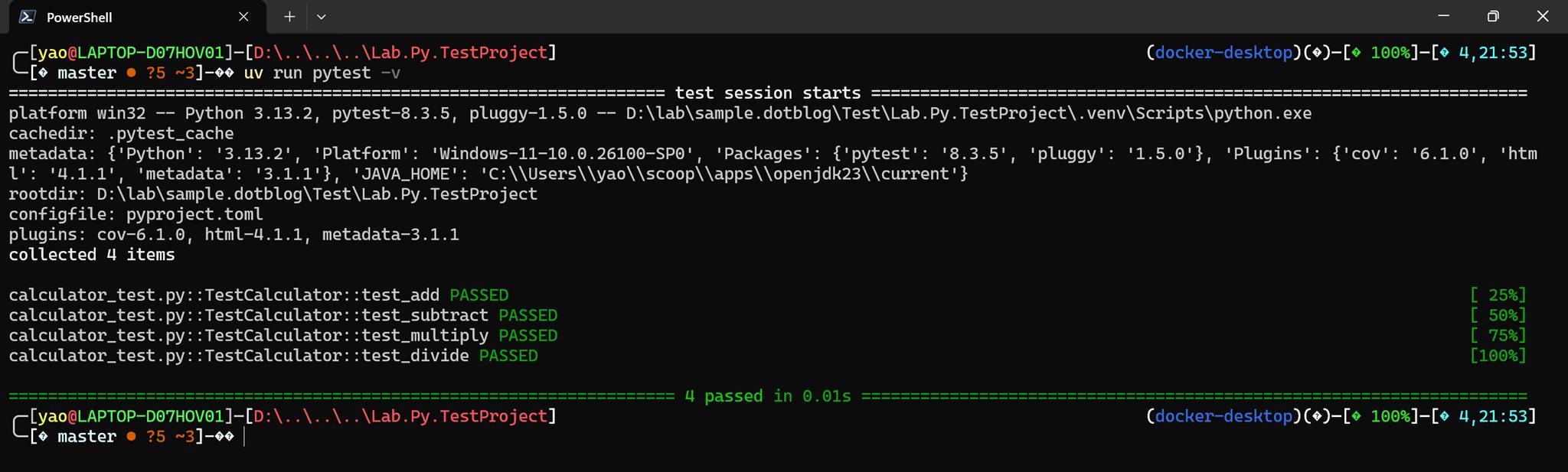
僅執行失敗的測試
uv run pytest --lf
產生 HTML 測試報告
在 python 專案安裝測試報告套件
uv add pytest-html
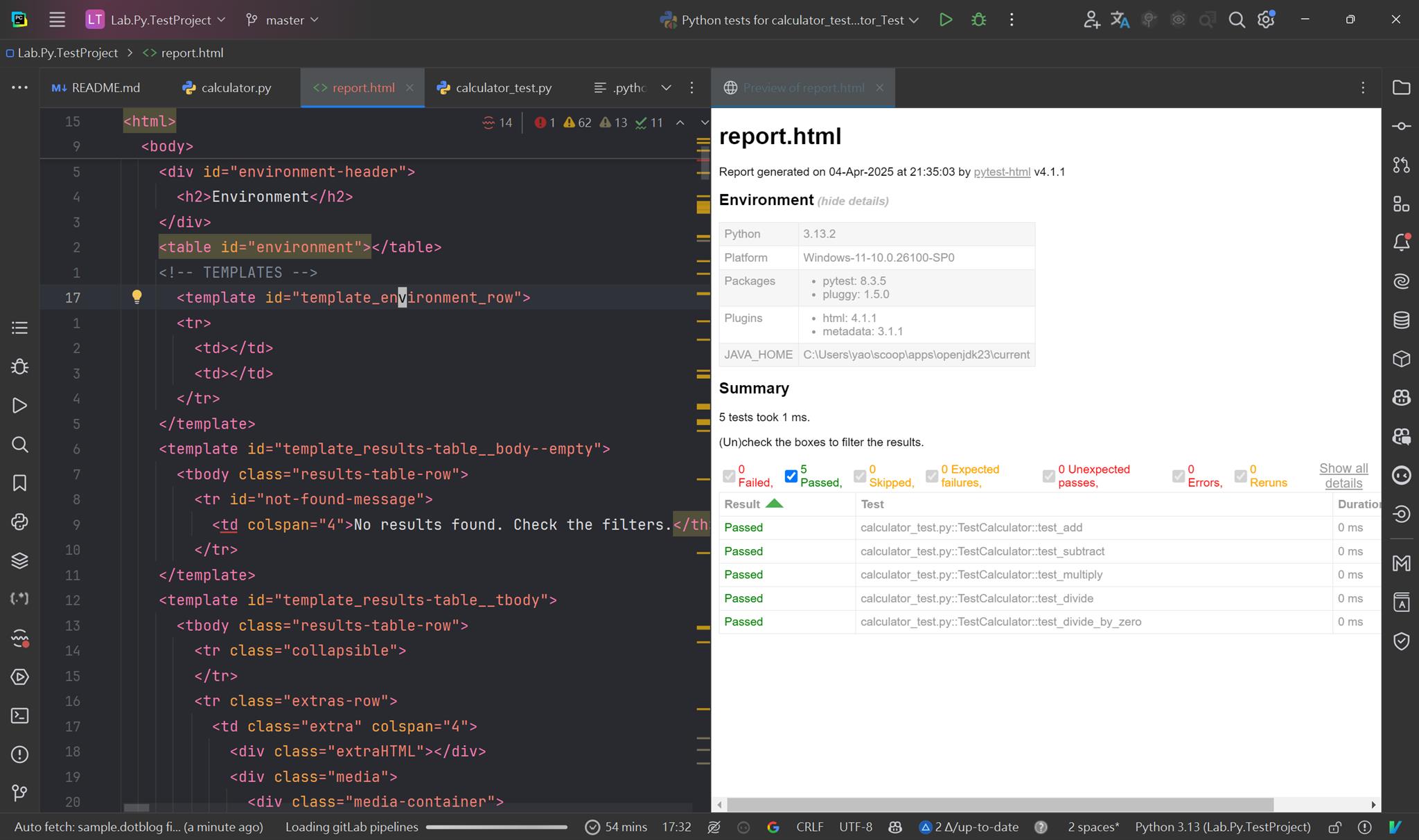
執行測試並輸出報告:
uv run pytest --html=report.html
report.html 效果如下
產生 Allure 測試報告
在作業系統安裝 allure
scoop install allure
在 python 專案安裝 allure-pytest 套件
uv add allure-pytes
執行測試並產生 allure result
uv run pytest --alluredir=allure-results
掛起 allure server
allure serve allure-results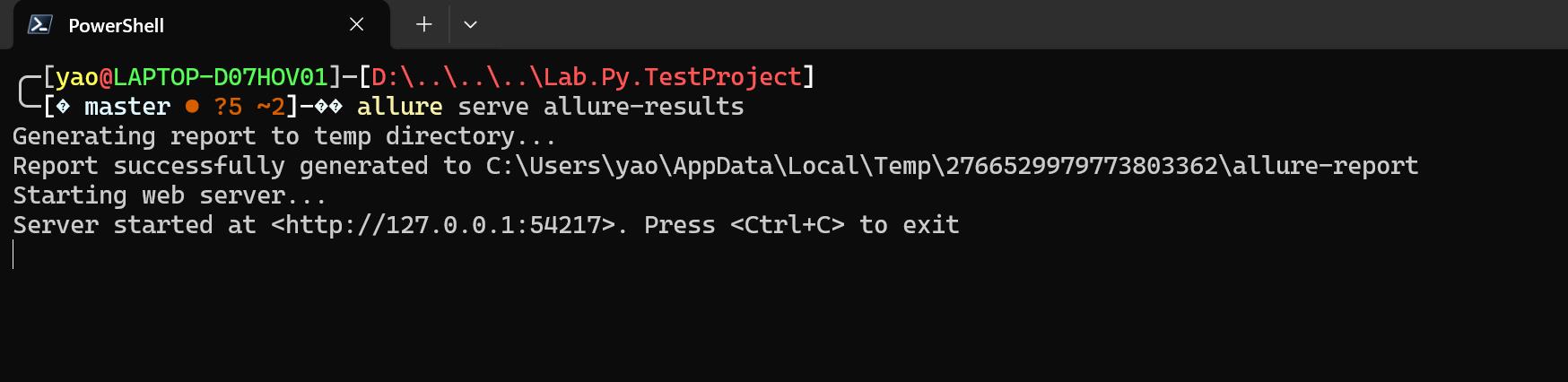
執行結果如下:
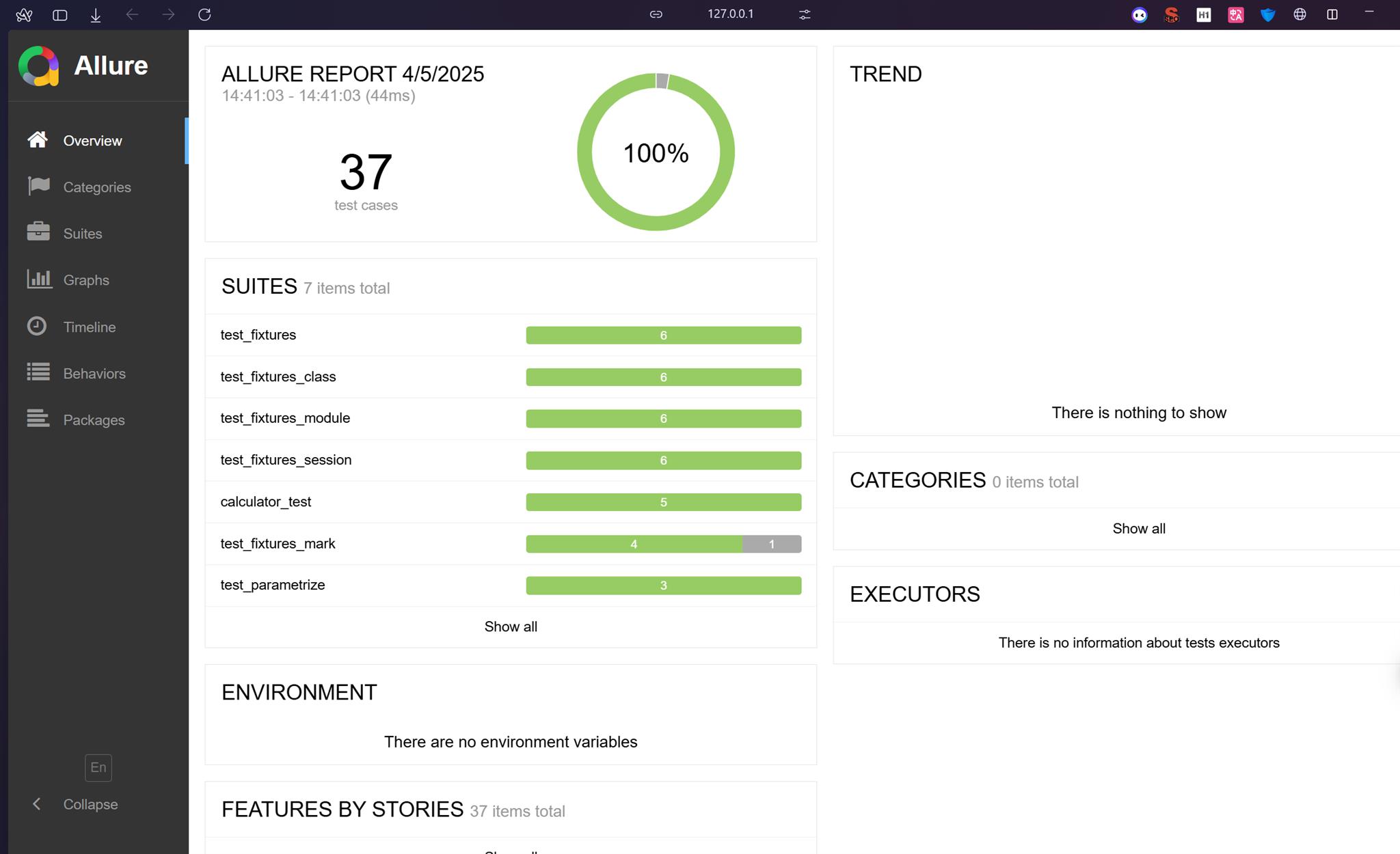
測試涵蓋率
uv run pytest --cov=calculator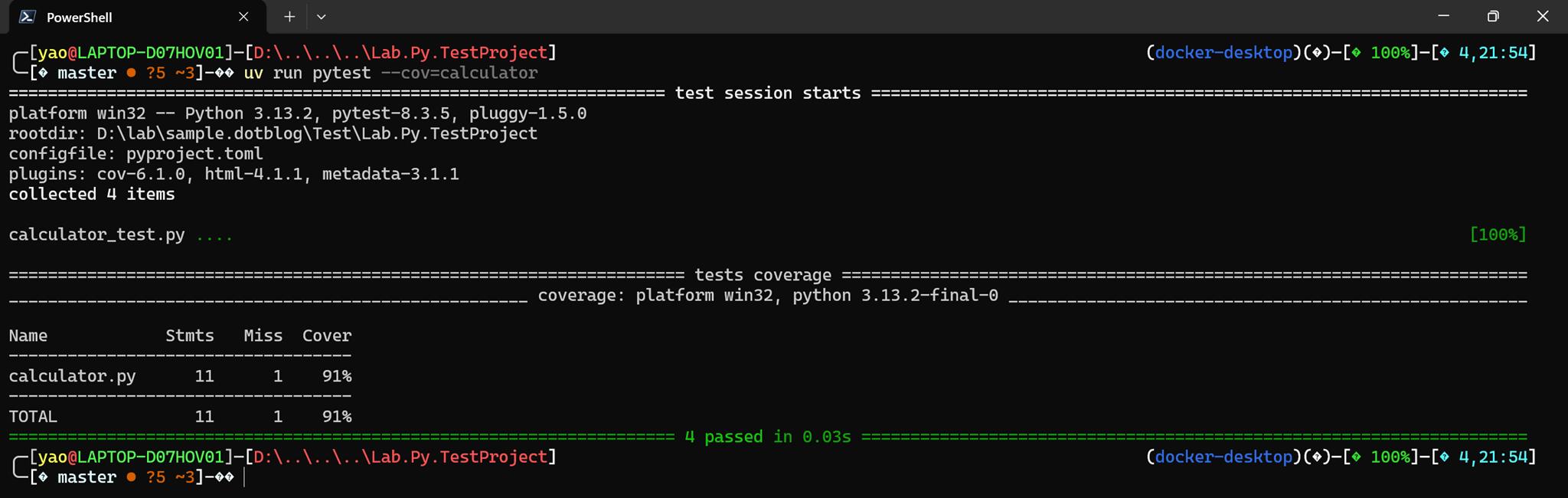
參數化測試
使用 裝飾子 decorator @pytest.mark.parametrize 定義傳入參數值、驗證值,就可以批次執行測試,類比 .NET 的測試框架 MsTest、XUnit、NUnit
# test_parametrize.py
import pytest
from calculator import Calculator
@pytest.mark.parametrize("first, second, expected", [
(2, 3, 5),
(-1, 1, 0),
(0, 0, 0),
])
def test_add(first, second, expected):
calculator = Calculator()
assert calculator.add(first, second) == expected
執行結果如下
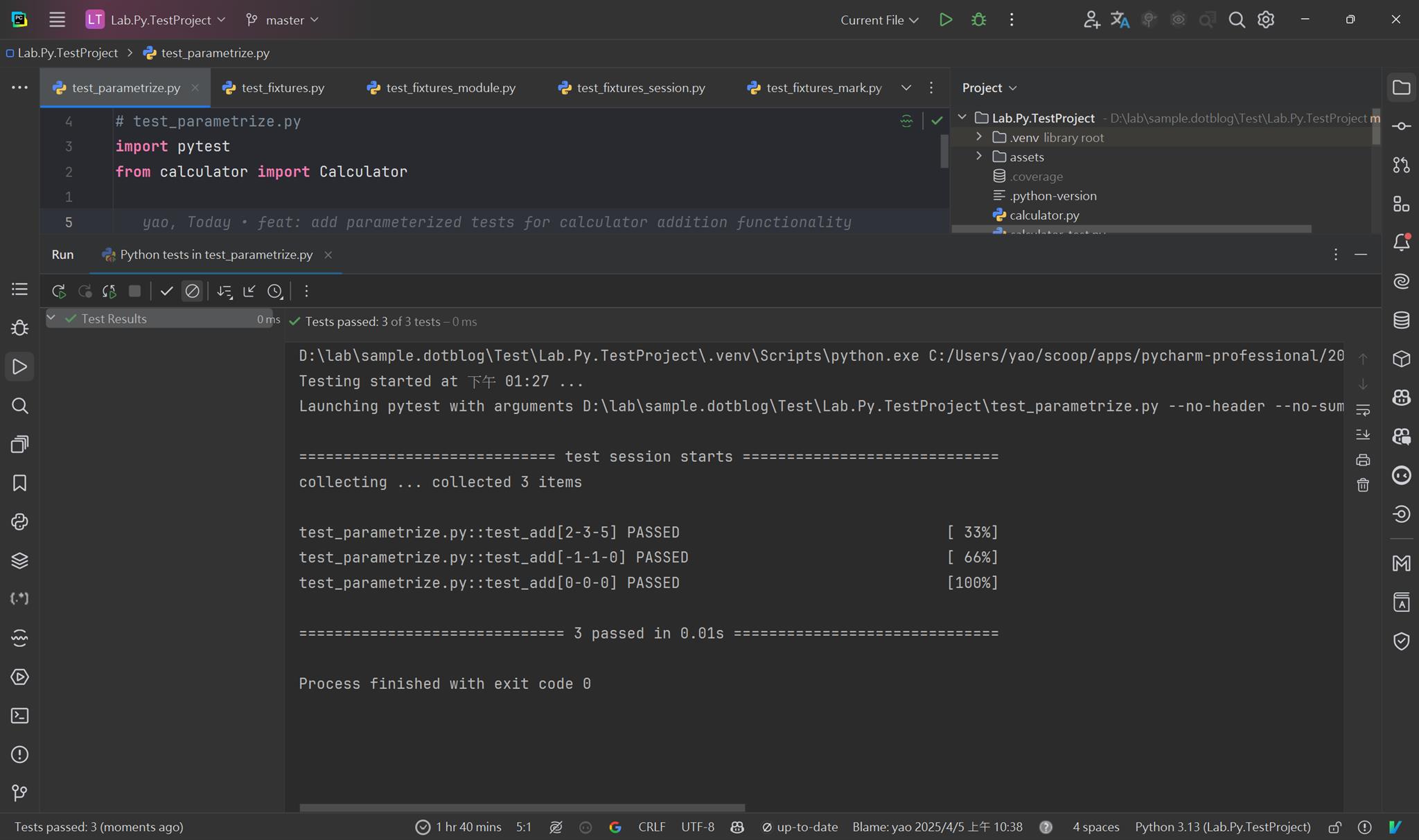
fixture/scope
fixture 是用來定義測試,需要共用資源的修飾子,共用的範圍 scope 有以下層級:
- function
- class
- module
- session
- 預設的 scope="function"
- 測試方法依賴 @fixture 方法,例如,setup_and_cleanup_function
每一個測試 function 執行前後設置及清理
當 scope="function",會在每一個 function 分別執行一次設置和清理
# test_fixtures.py
import pytest
from calculator import Calculator
@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
def setup_and_cleanup_function():
print("\n")
print("每一個 function 個別執行一次設定")
yield
print("\n")
print("每一個 function 個別執行一次清理")
def test_add_1(setup_and_cleanup_function):
target = Calculator()
assert target.add(2, 3) == 5
class TestCalculator:
def test_add(self, setup_and_cleanup_function):
target = Calculator()
assert target.add(2, 3) == 5
... 省略每一個測試類別 (class) 執行前後設置及清理
當 scope="class",會在第一個測試方法前執行一次設置,最後一個方法執行後執行一次清理
# test_fixtures_class.py
import pytest
from calculator import Calculator
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def setup_and_cleanup_module():
print("\n")
print("每一個 class 執行一次設置\n")
yield
print("\n")
print("每一個 class 執行一次清理\n")
def test_add_1(setup_and_cleanup_module):
target = Calculator()
assert target.add(2, 3) == 5
class TestCalculator:
def test_add_2(self, setup_and_cleanup_module):
target = Calculator()
assert target.add(2, 3) == 5
當前 .py 檔的 class 和 function 只執行一次設置和清理
當 scope="module",當前 .py 檔,class 和 function 只執行一次設置和清理
# test_fixtures_module.py
import pytest
from calculator import Calculator
@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def setup_and_cleanup_module():
print("\n")
print("當前 .py 檔,class 和 function 只執行一次設置\n")
yield
print("\n")
print("當前 .py 檔,class 和 function 只執行一次清理\n")
def test_add_1(setup_and_cleanup_module):
target = Calculator()
assert target.add(2, 3) == 5
class TestCalculator:
def test_add_2(self, setup_and_cleanup_module):
target = Calculator()
assert target.add(2, 3) == 5
... 省略
每一個測試 Session (package) 執行一次設置及清理
scope="session" 是在當前這個測試 Session (package) 的前後進行設置 / 清理工作,可以包含多個 .py 檔
# test_fixtures_session.py
import pytest
from calculator import Calculator
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def setup_and_cleanup_session():
print("\n")
print("每一個測試 session 只執行一次設置\n")
yield
print("\n")
print("每一個測試 session 只執行一次清理\n")
def test_add_1(setup_and_cleanup_session):
target = Calculator()
assert target.add(2, 3) == 5
class TestCalculator:
def test_add_2(self, setup_and_cleanup_session):
target = Calculator()
assert target.add(2, 3) == 5
... 省略
按下 F5 或是 Alt+F5 觀察,設置和清理的生命週期
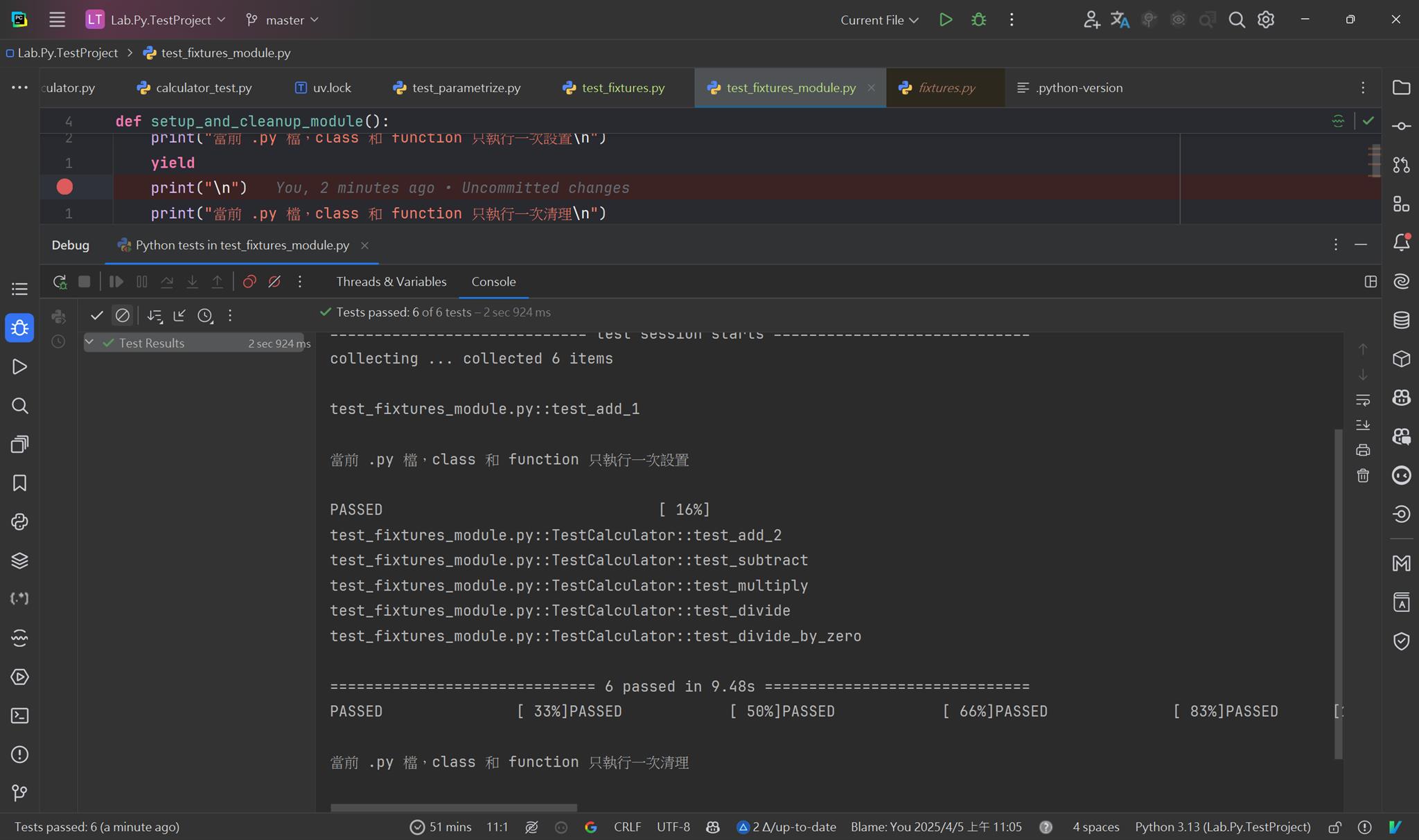
或是用以下腳本觀察
uv run pytest -v -s test_fixtures_module.py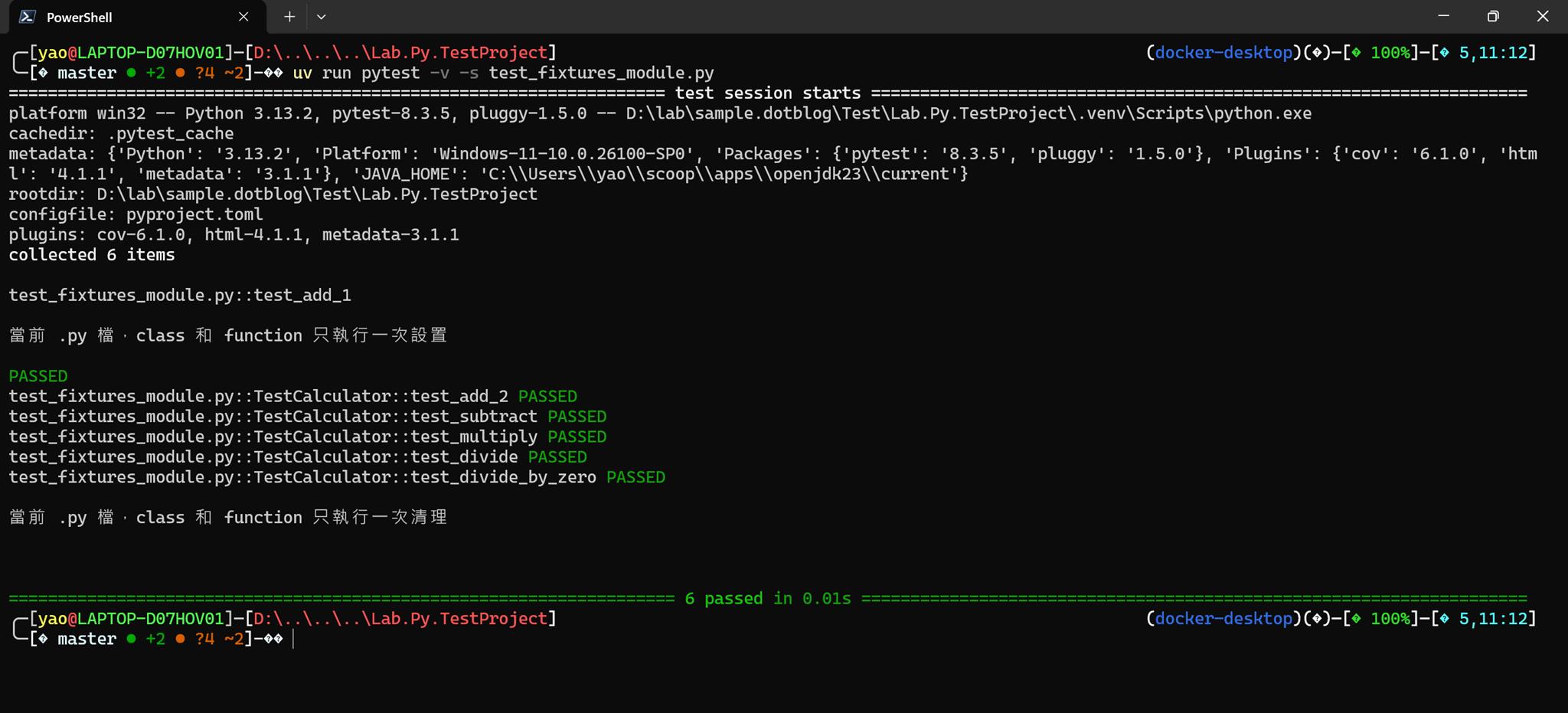
分類測試方法
當測試方法越來越多的時候,分類它們有助於閱讀跟查找、執行
當使用 @pytest.mark.demo 標記分類,demo 代表分類名稱
# test_fixtures_mark.py
import pytest
from calculator import Calculator
@pytest.mark.demo
class TestCalculator:
def test_add(self):
target = Calculator()
assert target.add(2, 3) == 5
def test_subtract(self):
target = Calculator()
assert target.subtract(5, 3) == 2
def test_multiply(self):
target = Calculator()
assert target.multiply(4, 3) == 12
def test_divide(self):
target = Calculator()
assert target.divide(10, 2) == 5
@pytest.mark.skip
def test_divide_by_zero(self):
target = Calculator()
with pytest.raises(ValueError):
target.divide(10, 0)
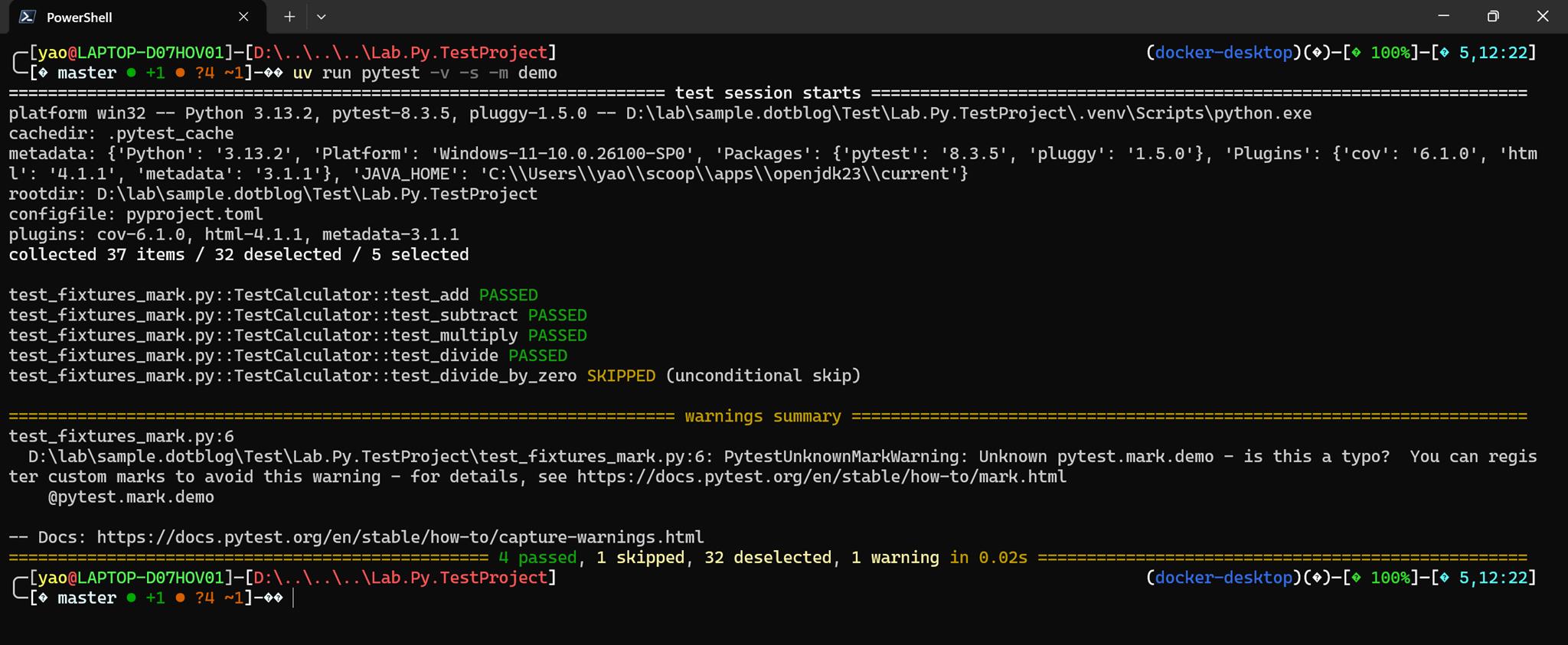
調用測試時,指定要執行哪一個分類,傳入 -m demo,這樣一來就只會執行 demo 類別的測試
uv run pytest -v -s -m demo
執行結果如下:
跳過測試方法
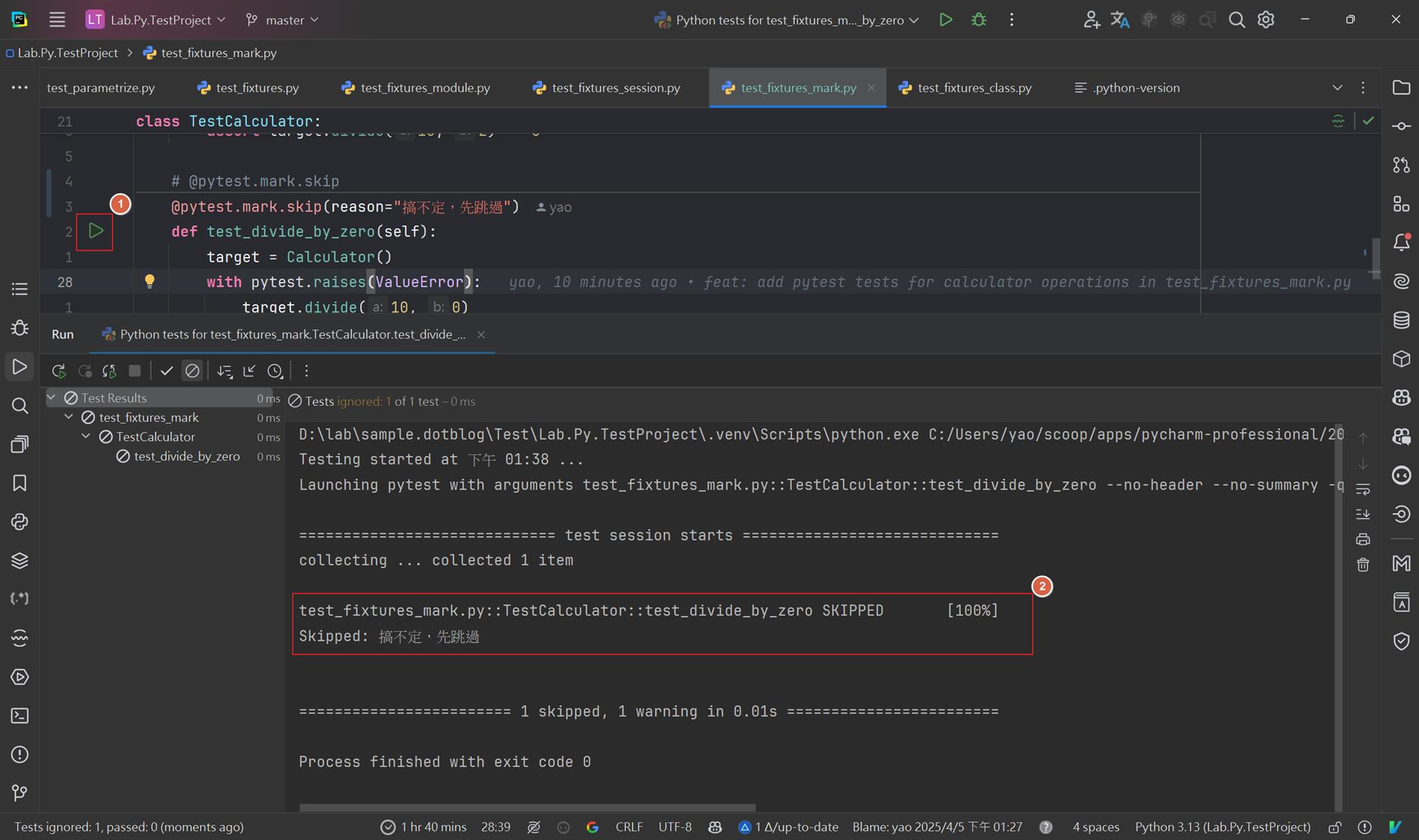
裝飾子 pytest.mark.skip,可以用來標記不執行,當執行測試時,會略過它
@pytest.mark.skip(reason="搞不定,先跳過")
def test_divide_by_zero(self):
target = Calculator()
with pytest.raises(ValueError):
target.divide(10, 0)
執行結果如下:
範例位置
https://github.com/yaochangyu/sample.dotblog/tree/master/Test/Lab.Py.TestProject
參考
https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/getting-started.html
若有謬誤,煩請告知,新手發帖請多包涵
Microsoft MVP Award 2010~2017 C# 第四季
Microsoft MVP Award 2018~2022 .NET