pytest-bdd 是用 python 實作 cucumber 的框架,有在寫測試的開發者,肯定不能錯過
開發環境
- Windows 11 Home
- Python 3.13
- PyCharm
- uv
- pytest-bdd 8.1.0
安裝環境
建立虛擬環境
uv venv
還原依賴套件
uv pip install -e .
或是安裝
uv add "pytest-bdd>=4.46.0"
pytest-bdd
根據 Gherkin/Cucumber 語言描述測試案例
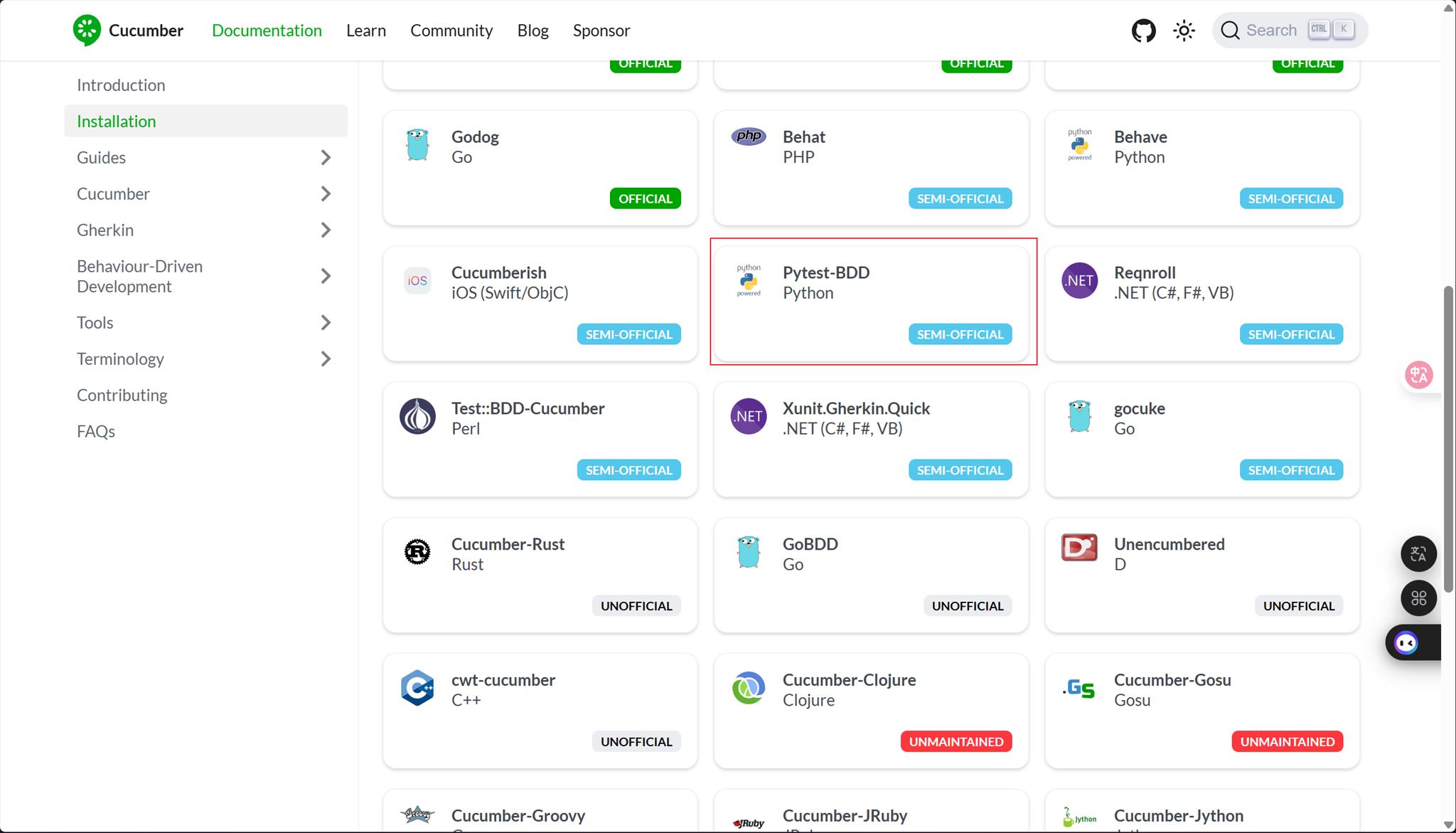
feature
#features/calculator.feature
測試步驟如下
Feature: 計算機基本運算
作為一個使用者
我想要使用計算機進行基本運算
以便能夠快速得到計算結果
Scenario Outline: 基本四則運算
Given 我有一個計算機
When 我輸入第一個數字 <num1>
And 我選擇運算符號 <operator>
And 我輸入第二個數字 <num2>
And 我按下 = 鍵
Then 我應該得到結果 <result>
Examples:
| num1 | num2 | operator | result |
| 5 | 3 | + | 8 |
| 10 | 4 | - | 6 |
| 6 | 7 | * | 42 |
| 20 | 5 | / | 4 |
....
alt + enter pycharm 開發工具會出現建立步驟的選單(create step definition),可以選擇新增步驟或是選擇已經存在的檔案
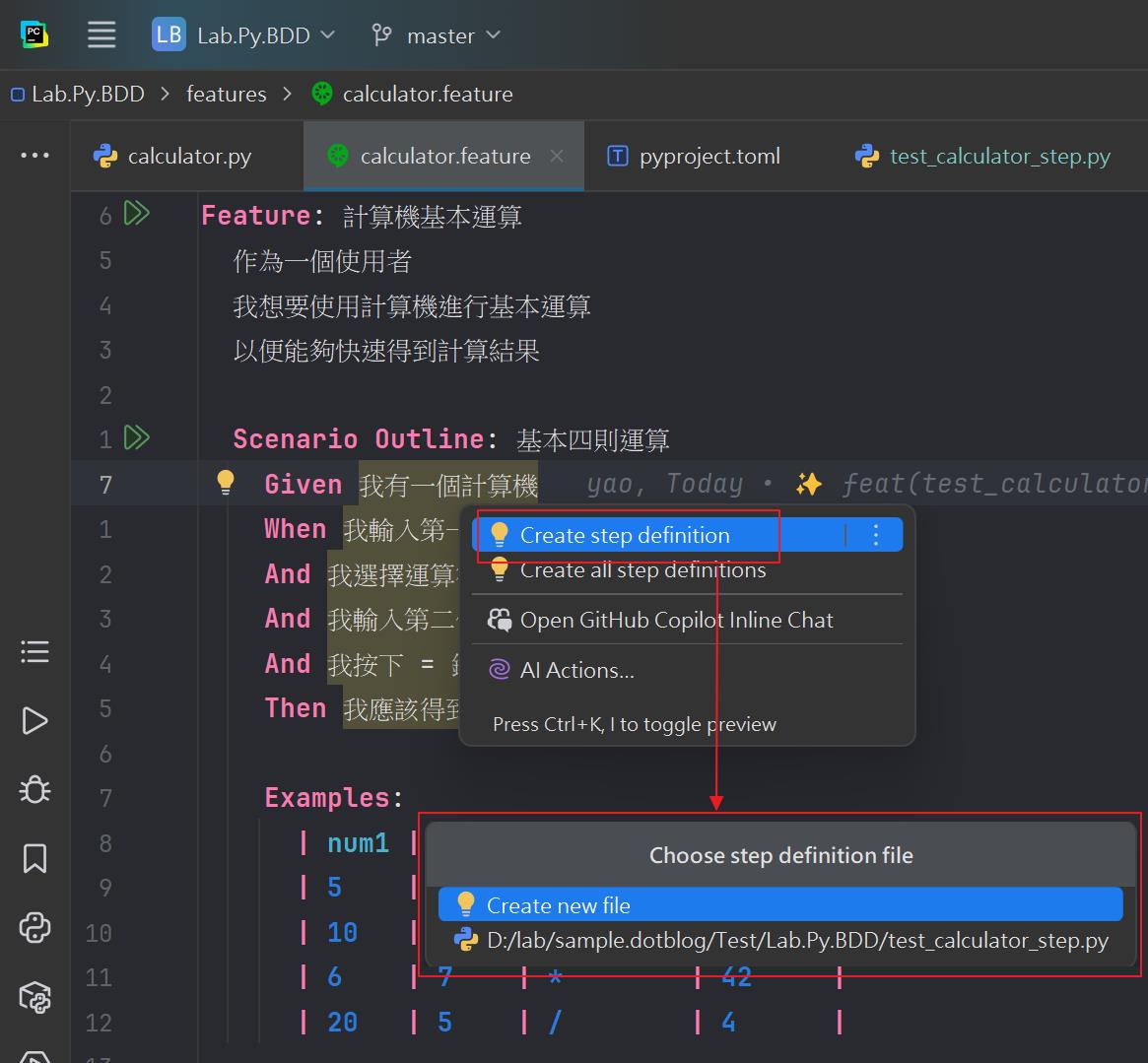
step
透過 IDE 產生一個空的 step
#test_calculator_step.py
@given("我有一個計算機")
def step_impl():
raise NotImplementedError(u'STEP: Given 我有一個計算機')
target_fixture
target_fixture 是一個裝飾器,用途:
- 用於 given step (@given 裝飾器 )
- 可被後續的 steps(when, then)使用,也就是 scenario 中共享狀態
- context 是字典,會透過它傳遞狀態
@given('我有一個計算機', target_fixture='context')
def 我有一個計算機(calculator):
return {'calculator': calculator}
第一個 step 還需要初始化被測目標物
@pytest.fixture
def calculator():
return Calculator()
連結 .feature 和 step
scenarios('./features/calculator.feature')
parsers.parse
- 用於從 Gherkin 語句中提取參數,支援多種格式化字串的解析,匹配 feature 檔案中的步驟
- {num1:d}
- num1 是參數名稱
- :d 表示這是一個整數(decimal)參數
@when(parsers.parse("我輸入第一個數字 {num1:d}"))
def 我輸入第一個數字(context, num1):
context['num1'] = num1context['num1'] = num1,將解析後 num1 放進 context 字典裡
接下來的 step,就是把資料放進 context,再拿出來運算
@when(parsers.parse("我輸入第一個數字 {num1:d}"))
def 我輸入第一個數字(context, num1):
context['num1'] = num1
@when(parsers.parse("我輸入第二個數字 {num2:d}"))
def 我輸入第二個數字(context, num2):
context['num2'] = num2
@when(parsers.parse("我選擇運算符號 {operator}"))
def 我選擇運算符號(context, operator):
context['operator'] = operator
運算
@when("我按下 = 鍵")
def 我按下鍵(context):
num1 = context['num1']
num2 = context['num2']
operator = context['operator']
calculator = context['calculator']
# 定義運算符對應的計算機方法
operatorMap = {
'+': calculator.add,
'-': calculator.subtract,
'*': calculator.multiply,
'/': calculator.divide
}
if operator not in operatorMap:
raise ValueError(f"不支援的運算符號: {operator}")
try:
# 直接從字典取得對應的方法並執行
result = operatorMap[operator](num1, num2)
context['result'] = result
except ValueError as e:
context['error'] = str(e)
最後的 step 就是 assert,驗證期望跟實際運算結果
@then(parsers.parse("我應該得到結果 {result:d}"))
def 我應該得到結果(context, result):
assert context['result'] == result
@then(parsers.parse('我應該看到錯誤訊息 "{error_message}"'))
def 我應該看到錯誤訊息(context, error_message):
assert context['error'] == error_message
執行測試
執行所有測試
pytest -v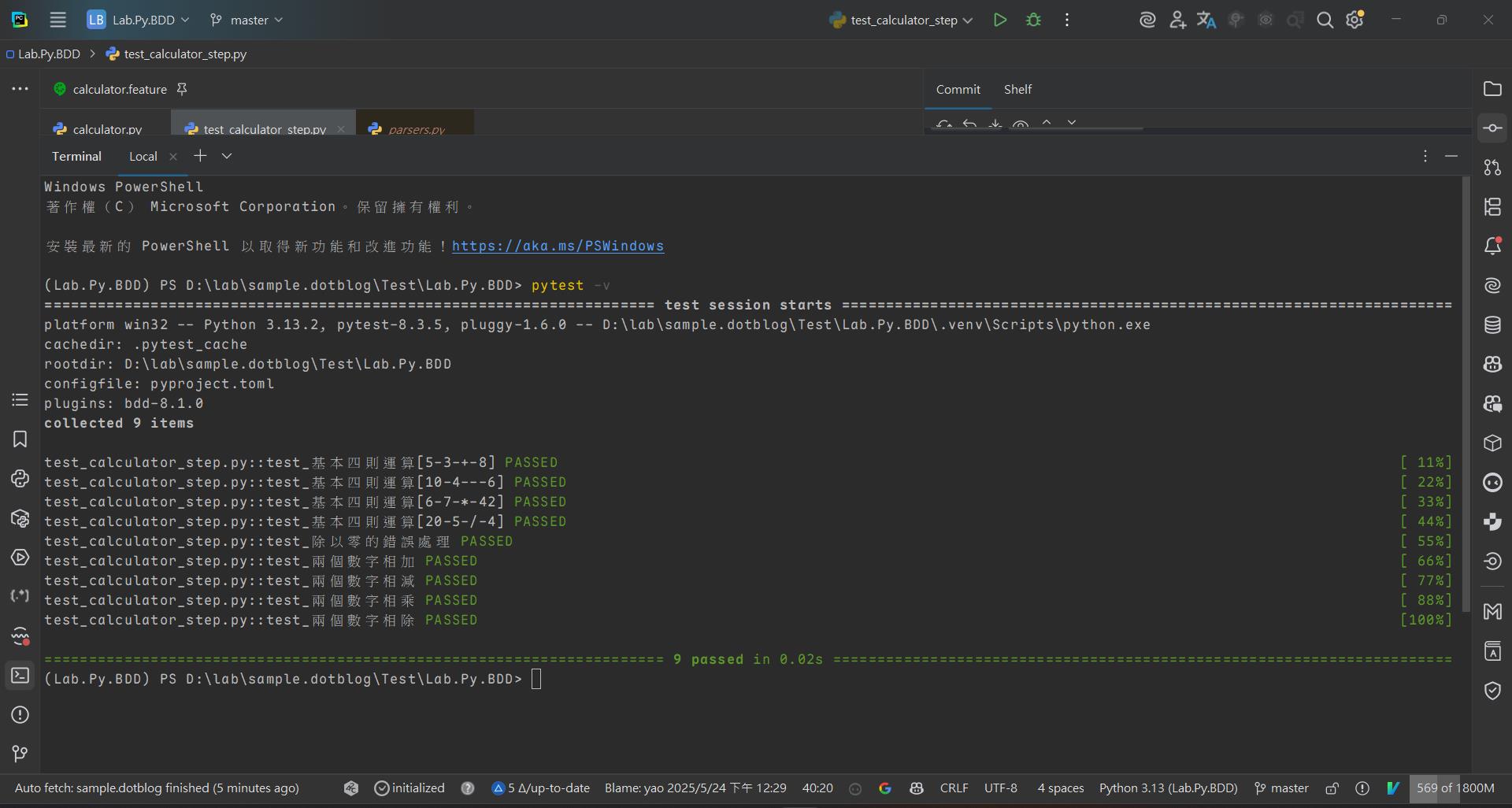
執行某一個測試
pytest -v -k "test_兩個數字相減"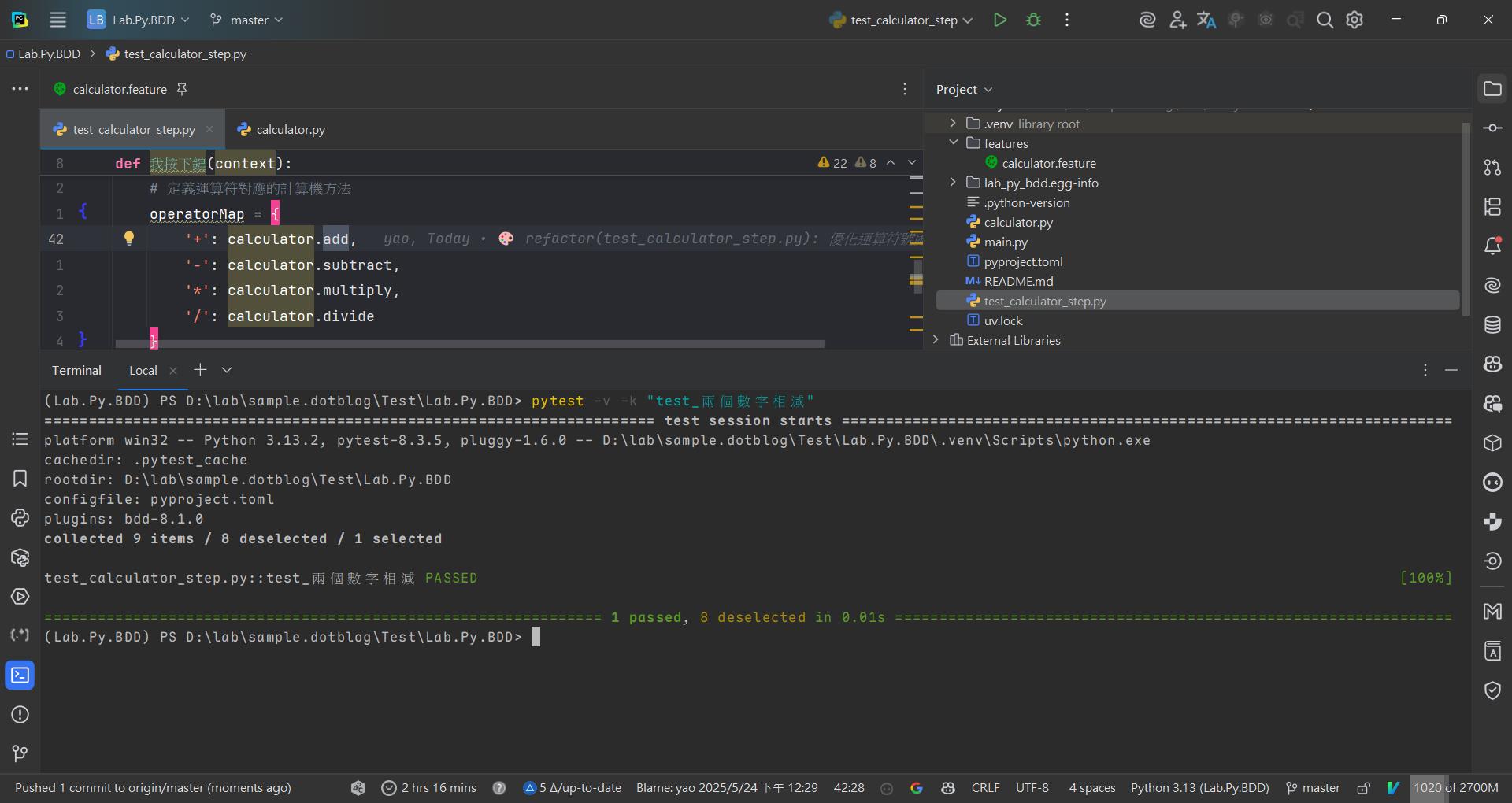
範例位置
若有謬誤,煩請告知,新手發帖請多包涵
Microsoft MVP Award 2010~2017 C# 第四季
Microsoft MVP Award 2018~2022 .NET